Languages can evolve into dialects over time. The more widely a language is spoken, the higher the chances are that new dialects will develop.
As time passes, dialects of the same language could diverge to such an extent that they could become distinct languages.
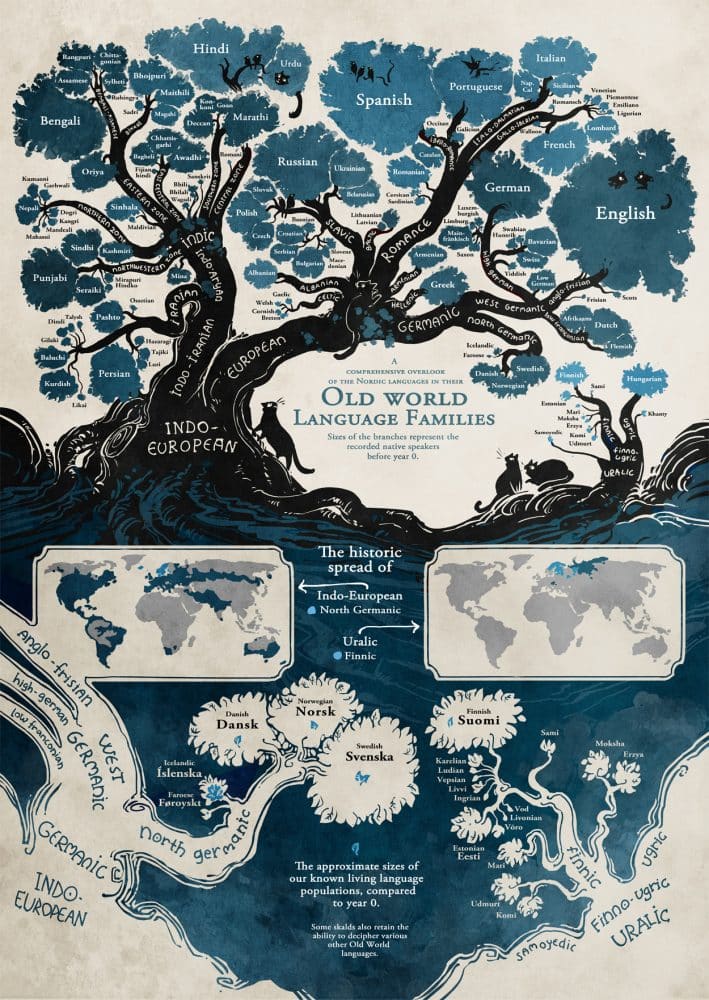
Based on this assumption about the development of languages, linguists have developed the so-called language trees. At the top of the tree is the parent language, while the branches underneath are the ‘offspring’ or related languages, which form a language family.
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family. With approximately 515 million native speakers and another two billion second language speakers, the Germanic languages are among the most widely spoken language families.
What’s more, the Germanic languages are a rather peculiar group of languages since they are simultaneously incredibly similar yet very different.
If you want to learn more about the Germanic language group, their origin, and their most common characteristics, keep reading!
In this blog, we have composed an in-depth guide to the Germanic languages.
Connect with your germanic customers in their native languages
Milestone helps you seamlessly translate content & localize your website, products, and services for more reach, better conversions, and greater sales.
What languages are Germanic?
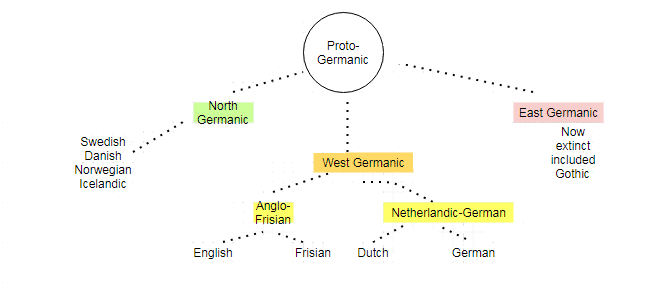
The Germanic languages are divided into three branches: West Germanic languages, East Germanic languages, and North Germanic languages.
Also read: Languages Spoken In Texas & Its Bilingual Education System
Let’s look at the full list of languages in each branch as well as the total number of speakers.
West Germanic
The West Germanic language branch is the largest of the three since it includes the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English, German, and Dutch.
West Germanic languages are spoken by about 500 million people natively.
The West Germanic language branch includes:
- English
- German
- Frisian
- Dutch
- Scots
- Afrikaans
- Yiddish
East Germanic
The East Germanic language branch consists of extinct Germanic languages, such as:
- Burgundian
- Vandalic
- Gothic
North Germanic
The most widely spoken North Germanic languages are Swedish, Norwegian, and Danish.
These languages are often called ‘Nordic’ or ‘Scandinavian’ since they are spoken as native languages throughout Scandinavia.
There are around 20 million native speakers of the Scandinavian languages.
- Danish
- Norwegian
- Swedish
- Faroese
- Icelandic
Also read: Nordic Languages: History, Similarities and Differences
Countries that speak Germanic languages
Germanic languages are spoken by more than 500 million native speakers and 2 billion second-language speakers.
Here are some of the countries where Germanic languages are most widely spoken:
English is undoubtedly the most widely spoken Germanic language. As of 2022, there were about 373 million native speakers of English.
The United States and India have the most English native speakers, with 306 million and 265 million, respectively. Pakistan is following with 104 million speakers. The United Kingdom, with its 68 million English speakers, is in 4th place, while Nigeria is in 5th place with 60 million.
There are six countries in which German is spoken: Germany, with more than 80 million speakers; Austria, with 8 million speakers; Switzerland, with 4.6 million speakers; and Belgium, with 75.000 speakers.
In addition to Luxembourgish and French, German is an official language in Luxembourg with 390.000 speakers. Europe’s fourth-smallest country, Liechtenstein, has 35,000 German speakers.
Dutch is also spoken in six countries: the Netherlands, Belgium, Curaçao, Sint Maarten, Aruba, and Suriname. It has 25 million native speakers.
Swedish is spoken in Sweden and parts of Finland and has about 10 million native speakers.
Norwegian is mainly spoken in Norway by 4.3 million speakers.
There are about 6 million Danish speakers located in Denmark, Schleswig-Holstein (Germany), the Faroe Islands, and Greenland.
Icelandic is spoken by only 314,000 speakers and is the official language of Iceland (as well as the Nordic Council).
Faroese is spoken as a first language by about 69,000 speakers, most of whom reside in the Faroe Islands and Denmark.
Also read: Things To Consider When Localizing For The German Market
Origin of Germanic languages
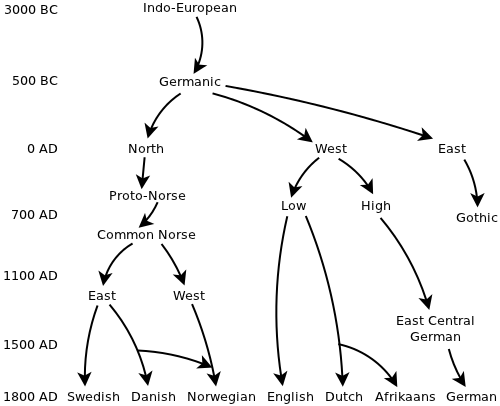
The Germanic languages are a subgroup of the Indo-European family tree. Proto-Indo-European, spoken more than 5,000 years ago, is considered to be the ancestor of all these languages.
About 4,000 years ago, Proto-Indo-European dialects evolved into a variety of daughter languages. One of them was an early version of Proto-Germanic, which probably came to southern Scandinavia around 1700 BCE. The language continued to evolve.
By 100 BCE, Proto-Germanic had split into three distinct languages: North Germanic, which is the ancestor of today’s Icelandic, Norwegian, Swedish, and Danish, West Germanic, or the ancestor of today’s English, Dutch, Afrikaans, and German; and East Germanic, the ancestor of several extinct languages, such as Gothic.
The West Germanic languages expanded in territory during and after the Roman period. They spread from the shores of the North and Baltic Seas to the southern and western parts of Europe.
Today, these territories include Germany and the Czech Republic to the South and the Netherlands, Belgium, and Great Britain to the West.
During the early Middle Ages, West Germanic dialects started evolving into the modern West Germanic languages we know today.
During the high Middle Ages, the same process took place among the North Germanic languages.
Comparison of Germanic languages: Similarities and differences
Germanic languages might have a common ancestor, but this doesn’t necessarily mean that they share a lot in common.
As you will see, there are quite a few differences, albeit rather subtle sometimes, between the members of this language group.
Alphabet
All Germanic languages use the Latin alphabet. However, one should keep in mind that there are additional symbols for each language.
In German, there are the umlauts: ü, ä, ö.
In Scandinavian languages, there are letters such as Å or Ø.
Also read 10 Interesting Facts About Greek: Origin And Evolution.
Verb Conjugation
All Germanic languages share a common feature when it comes to verb conjugation. There is a differentiation between “weak” and “strong” verbs.
Weak verbs are conjugated by adding a particular ending to the verb. For instance, the -ed ending of the verbs in English when used in the past simple tense: He painted a picture.
Strong verbs, on the other hand, change their form when used in the past tense. In German, strong verbs are quite common. The verb ‘helfen,’ meaning ‘to help’ changes to ‘half’ in its past simple form.
Grammar
Regarding grammar, the Germanic languages exhibit the same sentence structure. Germanic languages follow an S-V-O (subject-verb-object) sentence order.
German is an exception in that regard since the subject and object can change their positions in the sentence. However, the verb always stays in the second position.
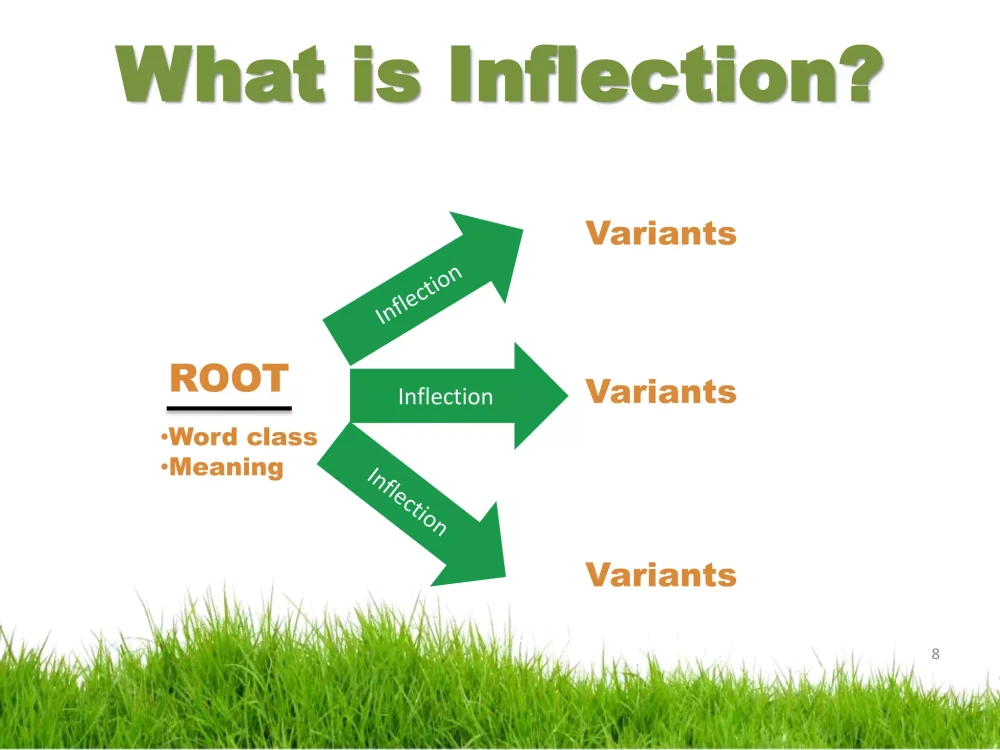
Inflection
What’s more, inflection is very common among Germanic languages.
Inflection is when endings are added to words to show certain grammatical roles.
For instance, in English, we add an -s ending to nouns to denote plural forms.
German, Norwegian, Swedish, Danish, and Dutch also have particular endings for denoting plural forms, but they are much more complex than in English.
Three-Gender System
The three-gender system is a widespread similarity that almost all Germanic languages share.
Languages like German and Danish differentiate between three grammatical genders: masculine, feminine, and neuter. Thus, for example, in German, “a table” is considered masculine while “a pocket” is feminine.
There are a few exceptions, though. For example, in mainland Scandinavia, this three-gender system is reduced to a common-neuter distinction. In English, genders are only used for people and pets.
Also read: German vs Russian: Which Language Has a Better Future?
Grimm’s Law
All Germanic languages have undergone the First Germanic Sound Shift, also known as Grimm’s Law.
According to Grimm’s Law, certain Indo-European consonants (such as stops like “p,” “t,” and “k”) have changed the Germanic languages that are not seen in other languages, such as Greek or Latin.
Also read: Top 10 Subtitling Companies : How To Choose The Right One
Examples include “p” becoming “f” so that the Latin word “pater” corresponds to English “father” and German “Vater.” The principle was described by Jacob Grimm, and thus, it was named after him.
In other words, every one of these languages has changed its use of consonants. These changes resulted in the creation of a unique phonological structure that is common only to the Germanic languages.
Vowel Sounds Variety
All Germanic languages exhibit great vowel variety.
For example, English has only five representative vowels (or letters); however, the way that these vowels can be pronounced is quite diverse.
Other Germanic languages also share this unique characteristic. Swedish has about 17 vowels while German and Dutch have 14 vowel sounds.
Connect With Your Germanic Customers In Their Native Languages
Milestone helps you seamlessly translate content & localize your website, products, and services for more reach, better conversions, and greater sales.
Germanic languages vs. Romance languages
The Romance languages are another branch of the Indo-European language family, which includes Italian, French, Portuguese, and Spanish.
As you can imagine, Romance and Germanic languages are quite different since they belong to different branches of the same family. However, they stem from the same language, Proto-Indo-European.
Thus, they are likely to share some similarities. But is that so?
One of the main differences between these language groups is their origin. Romance languages evolved from Vulgar Latin, while Germanic languages stem from Proto-Germanic.
As a result, one can observe very noticeable differences between the languages of these groups regarding pronunciation, grammar, and the meaning of the words.
Also read: 10 Untranslatable German Words
Is English Germanic?
English is a Germanic language, and yet it is not a very ordinary member of this language group.
On the one hand, English has a lot of similar words to Germanic languages due to their common roots. Take, for example, the word ‘house’ in English, which translates to ‘Haus’ in German, to ‘huis’ in Dutch, and to ‘hus’ in Swedish, Norwegian, and Danish.
On the other hand, English shares a great deal of vocabulary with Romance languages such as French and Italian. Some examples include words like ‘diva,’ ‘solo, ‘chef,’ ‘dessert,’ and ‘debut.’
Then you might be wondering why English is a Germanic and not a Romance language.
According to linguists, English is a Germanic language since its overall structure is more similar to Germanic languages than Romance languages.
As for the similarities in the vocabulary, these can be easily explained by the fact that French was spoken on the territory of England for 300 years during the Norman invasion.
During these three centuries, the English language was greatly influenced by French, and we can see that even today.
In English, there are a lot of words with the same meaning, but different origins. For instance, ‘rage’ and ‘anger’ mean the same thing, however, the first one has a Latin origin while the latter is a Germanic word.
Also read: German vs. Polish: How Different Are These Two Languages?
Conclusion
The Germanic languages are a rather small, yet very intriguing group.
While these languages share a lot of similarities, each one of them has unique features that set it apart from the other members of the group.
What’s more, Germanic languages, such as English and German, are very widely spoken. Others, like Norwegian, Swedish, Danish, and Dutch, have a lot fewer native speakers.
Indeed, the Germanic languages are a unique and diverse group of languages!
Connect With Your Germanic Customers In Their Native Language
Milestone helps you seamlessly translate content & localize your website, products, and services for more reach, better conversions, and greater sales.