The Latin script has left an incredible mark on our human civilization with over 3,000 languages employing it.
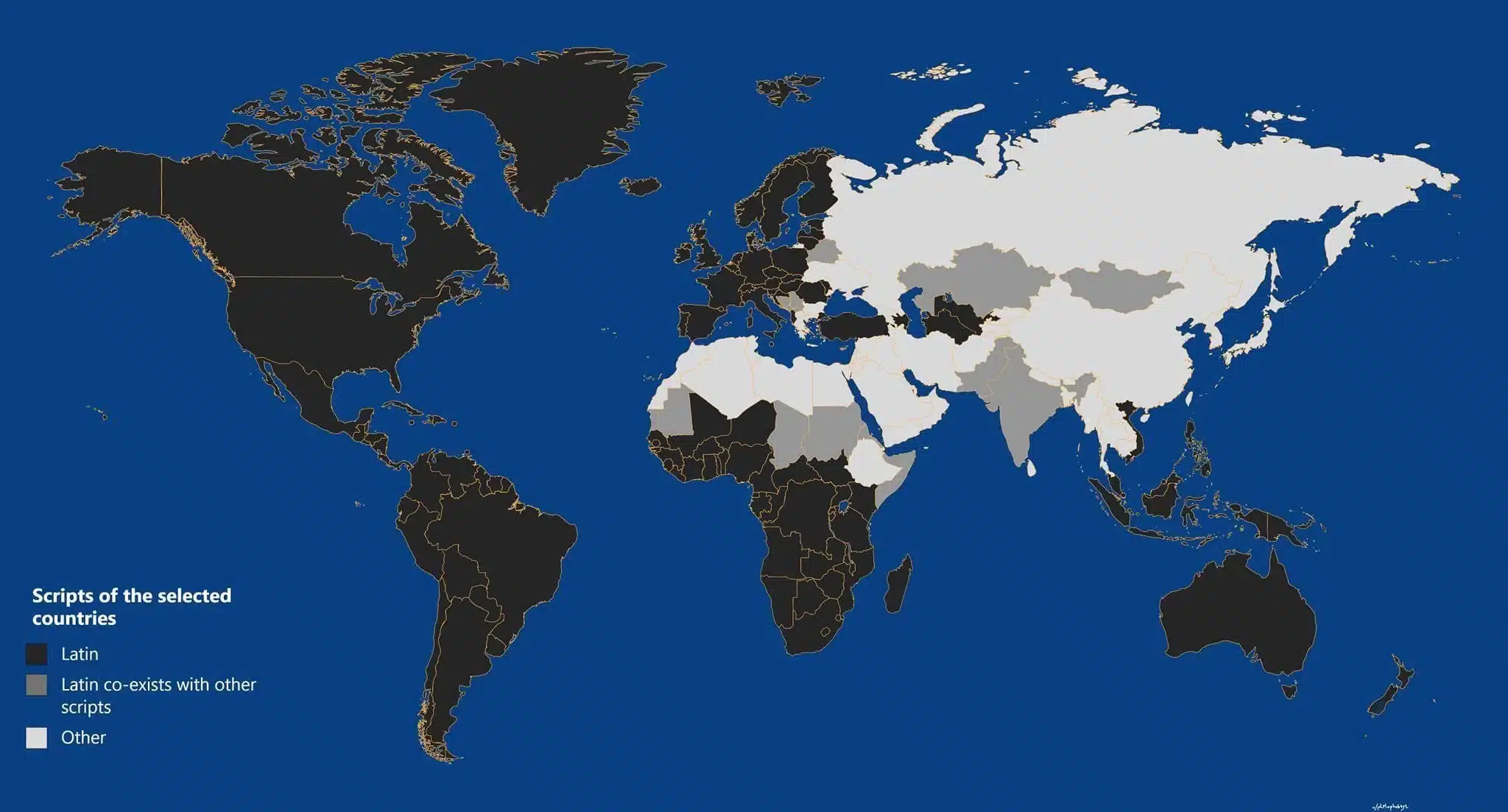
The Latin script is the most widely used in the world with nearly 70 per cent of the world’s population utilizing it.
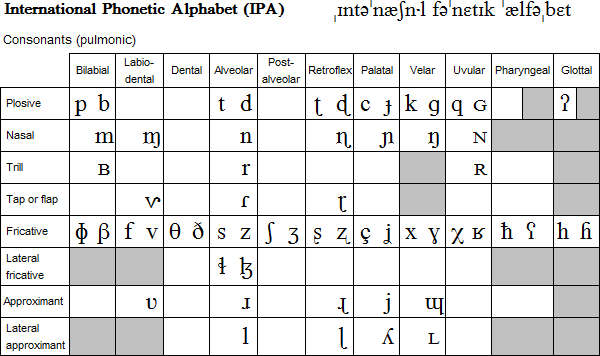
What’s more, it is the basis for the International Phonetic Alphabet, which is used to denote the phonetic systems of all languages.
How the Latin alphabet developed, however, is quite a fascinating story! The Latin script emerged in ancient Italy and has spread across countries, continents, and cultures throughout the centuries.
In this blog, we’re going to delve into the rich history of this alphabet while also exploring its evolution and current usage, transcending geographical and cultural boundaries.
Are you Looking for professional translation services?
Milestone helps you accurately translate your documents, websites, apps, and more in 70+ languages
Origin and Evolution of Latin
The Latin alphabet is sometimes referred to as the Roman alphabet. This script has a long, rich history that can be traced back to ancient times.
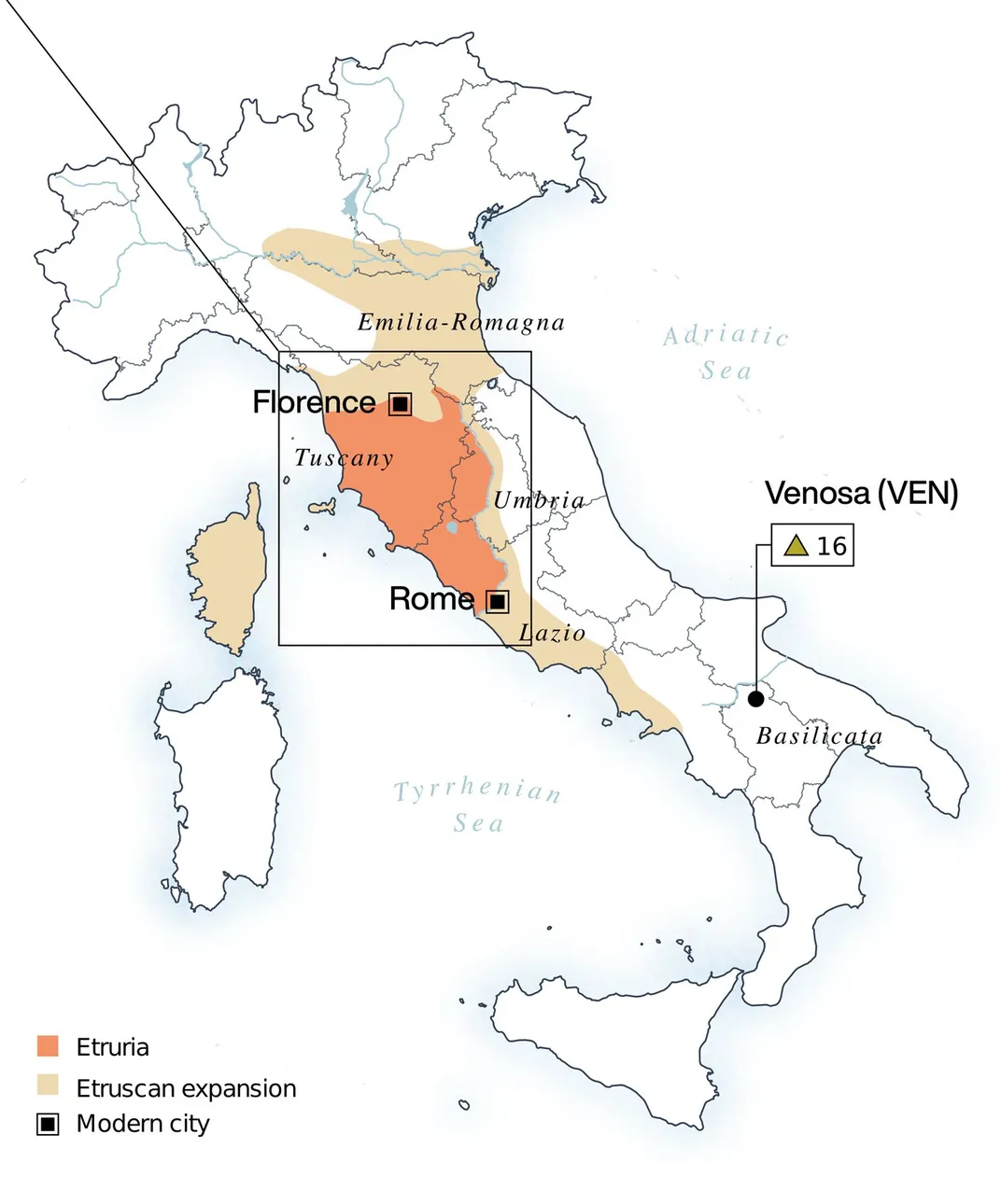
Its origins are believed to be in the Etruscan alphabet, which was derived from the Greek alphabet around the 7th century BC.
The Etruscans were an ancient civilization on the territory of ancient Italy. They adapted the Greek script to their language and culture. This adaptation marked the beginning of the Latin alphabet.
The earliest known form of the Latin alphabet consisted of 21 letters. The letters J, U, and W were added only later and thus, were not part of these initial variations.
In the 5th century BC, the ancient Romans modified and expanded the Latin alphabet to suit the needs of their language – Latin. Over time, as the Roman Empire and its power expanded across Europe and beyond, the Latin script evolved and spread across its territory.
During the Middle Ages, the lowercase letters emerged. Previously, the Latin alphabet was written only in uppercase letters.
As handwriting became more prevalent, this distinction between lower and uppercase letters became necessary for practical reasons.
Throughout its history, the number of letters in the Latin alphabet has fluctuated due to many factors, such as cultural influence, linguistic change, and the adaptations of letters for new languages.
Letters, such as J, U, and W were introduced to the alphabet at different points in history to fill in gaps in terms of proper representation of sounds.
The letter J originally was a variant of the letter I. Both of these letters were initially used interchangeably until J became established as a separate letter.
Similarly, the letter U evolved from V to represent both the consonantal and vocalic sounds associated with it. The letter W originated as a ligature of two Vs (VV) and was only later recognized as a distinct letter to represent the /w/ sound.
Overall, the Latin alphabet has a long history, beginning in ancient Italy and spreading to all corners of the globe. Today, the Latin alphabet continues to serve as the foundation for countless languages and writing systems around the globe.
Also read: 10 Interesting Facts About Greek: Origin & Evolution
Languages that use the Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet serves as the primary writing system for a wide variety of languages, especially across Europe:
- Romance languages, including Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese, and Romanian;
- Germanic languages, such as English and German;
- Slavic languages like Polish, Czech, and Croatian.
Additionally, some languages spoken in Africa, Asia, and the Americas have adopted the Latin script:
- Languages in the ‘Greater’ Middle East: Many countries in the Middle East and North Africa have adopted the Latin alphabet alongside or instead of the Arabic script.
For instance, in 1928, as part of Atatürk’s Reforms, the Latin alphabet was adapted to match the phonetic system of the Turkish language. Since then, Turkish has been written with the Latin script instead of the Arabic one. - African languages: Several African languages utilize the Latin alphabet, including Swahili, Hausa, Yoruba, and Igbo.
- Southeast Asian languages: Southeast Asian languages, such as Indonesian, Malay, Tagalog, and Vietnamese, have adopted the Latin alphabet as well.
- Indigenous American languages: Some indigenous languages like Quechua, Nahuatl, and Guarani have been using the Latin alphabet as a way to preserve and revitalize them.
- Pacific Island languages: Hawaiian, Samoan, and Fijian also utilize the Latin alphabet.
- Indigenous Australian languages: Indigenous Australian languages, such as Warlpiri and Arrernte, have also been transcribed using the Latin alphabet.
Undoubtedly, the Latin script is ubiquitous, which in turn underscores its flexibility and adaptability to diverse linguistic and cultural contexts across all continents.
Also read: What Are The Fastest Growing Languages?
Variations in the Latin alphabet usage
The Latin alphabet exhibits a large number of variations in its usage across different languages. Here is an overview of the most common ones:
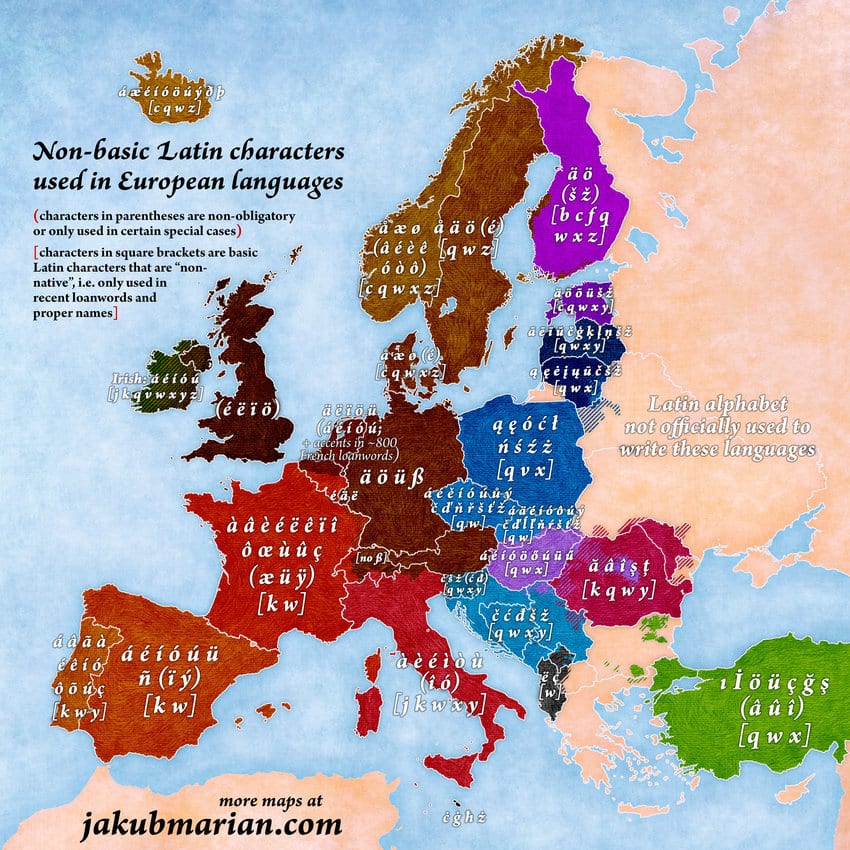
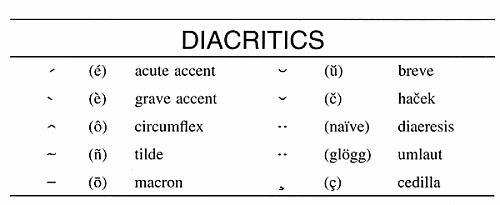
Diacritics: Diacritics are marks, which are added to letters to alter their pronunciation. Diacritics such as accents, umlauts, and cedillas are common in languages like French, Spanish, and German. These marks serve to distinguish between distinct sounds or indicate stress patterns.
Inclusion or omission of letters: For example, English uses the full set of 26 letters. Other languages, however, may include additional letters, which represent specific sounds unique to their phonetic systems. Conversely, some languages may eliminate certain letters from the alphabet to accommodate phonological differences.
Differences in arrangement and pronunciation of letters: Digraphs (two letters representing one sound) or phonetic shifts in pronunciation can result in variations in the way letters are arranged or pronounced in a language.
For example, in the Spanish greeting “hola” the initial letter H is not pronounced while in the German word “Haus” the letter H is pronounced as a /h/sound.
Similarly, in the German word “Vogel” the letter V corresponds to the sound /f/ while in English the same letter is pronounced as a /v/ sound as in the word “voice.”
As you can see, these variations reflect the diverse linguistic and cultural contexts in which the Latin alphabet is utilized. What’s more, they highlight the ability of the Latin script to adapt to various languages and phonetic systems.
Also read: 10 Fascinating Facts About Spanish
Reliable Language Translation Services
Milestone helps you accurately translate your documents, websites, apps, and more in 70+ languages
Latin alphabet vs Greek alphabet
The Latin and Greek alphabets are among the most influential writing systems, especially in Europe. Both have played a significant role in shaping two of the greatest civilizations on the Old continent – the Ancient Greek and the Roman civilizations.
While they share common origins, they have evolved independently and thus, exhibit several distinct differences:
Number of letters: The Greek alphabet consists of 24 letters, while the Latin alphabet typically has 26 letters. Both scripts utilize consonants and vowels, but the specific characters and their phonetic values, or pronunciation, vary distinctly.
Presence of diacritics: The Greek alphabet utilizes various diacritical marks, such as accents, breathing marks, and iota subscripts to indicate stress, aspiration, and vowel length. Indeed, in the Greek alphabet, these marks are essential for ensuring proper pronunciation of the sounds. In addition, they play a huge role in determining the meaning of words.
In the Latin script, in contrast, diacritics are occasionally employed in various adaptations of the script. Nevertheless, these marks are much less common than in the Greek alphabet.
Usage: The Greek alphabet is primarily associated with the Greek language. In contrast, the Latin alphabet has a broader scope of usage, serving as the basis for numerous languages across Europe, the Americas, Africa, and Asia.
All in all, despite these differences, both the Latin and Greek alphabets have left their mark on human civilization by facilitating education, sciences as well as communication.
Also read: Germanic Languages: Origin, Similarities & Differences
Challenges with adapting the Latin alphabet to non-Latin languages
Adapting the Latin alphabet to languages, that do not stem from Latin, can pose several challenges:
Phonemic Differences: Languages that do not have Latin roots may contain phonetic sounds that do not exist in the Latin alphabet. Adapting the Latin alphabet to represent their phonetic systems accurately can be complicated and often requires the addition of diacritics or the creation of new letter combinations.
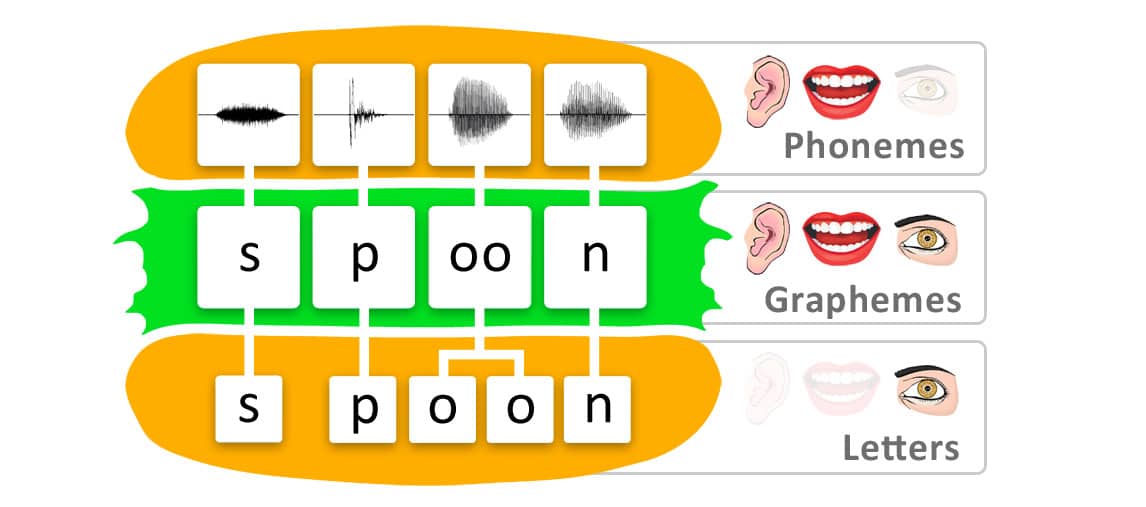
Grapheme-Phoneme Correspondence: Grapheme-Phoneme correspondence means that individual letters, or letter strings, represent an individual sound. For instance, in the verb “fly” the letter Y corresponds to the sound /ai/.
When it comes to adapting the Latin script, it might turn out that non-Latin languages have different grapheme-phoneme correspondences compared to Latin-based languages.
This in turn could result in potential confusion and ambiguity.
Character Limitations: As you already know, the Latin alphabet contains only 26 letters. These may not be enough to represent all the sounds in non-Latin languages accurately.
This in turn can result in the need for additional letters, diacritics, or modified letter forms to adequately capture the phonetic system of a language and its sounds.
Orthographic Conventions: Every language has its traditions and thus, languages often have their unique orthographic conventions. These may include specific spelling rules, punctuation, and word formation.
Adapting and incorporating these conventions to the Latin script while preserving the originality and traditions of the language’s written form can be challenging. What’s more, it may require significant modifications.
Technology and Accessibility: Adapting the Latin alphabet to non-Latin languages in digital settings can present technological challenges.
These challenges could range from font support and text input methods to compatibility across software and devices.
Ensuring widespread accessibility and usability of Latin-scripted non-Latin languages requires considerable investment in technological infrastructure and standards. What’s more, the establishment and regulation of these might be time-consuming as well.
Indeed, the adaptation of the Latin script to non-Latin languages poses quite a few challenges. Nevertheless, one should not overlook the fact that these adaptations have happened numerous times across the centuries, languages, and cultures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, throughout its long history, the Latin alphabet has demonstrated on numerous occasions its flexibility and adaptability.
Being currently used by thousands of languages around the globe, there are countless variations of the Latin script.
And despite the challenges that its adaptation may pose, this alphabet remains as popular as ever before!
Are You Looking for professional Market Translation Services?
Milestone helps you accurately translate your documents, websites, apps, and more in 70+ languages