The EU CLP Regulation EC No 1272/2008 (Classification, Labelling, and Packaging) is a key directive that sets requirements for the safe handling and communication of chemical hazards in the European market. This regulation outlines specific labelling, classification, and packaging guidelines that manufacturers must follow to ensure the safety of consumers, workers, and the environment.
Manufacturers, distributors, and importers must provide translated labels, safety data sheets, and hazard statements to meet legal requirements in each country where their products are being sold or used.
This blog highlights the translation requirements for CLP compliance in detail, providing insights into what needs to be accurately translated, the legal responsibilities of manufacturers regarding multilingual documentation, and best practices to ensure compliance across different languages and markets.
Looking for Chemical Translation services ?
Milestone works with native translators with domain expertise to accurately translate your documents into 70+ languages. We provide translation certificates accepted by authorities across the globe.
What is the CLP Regulation EC No 1272/2008?
The EU CLP Regulation EC No 1272/2008 (Classification, Labelling, and Packaging) is a European Union regulation that governs the classification and labelling of chemical substances and mixtures. It is Regulation EC No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council, and it has been in effect since January 20, 2009.
This regulation is designed to ensure the safe use of chemicals by setting clear guidelines for how they are classified, labelled, and packaged based on their hazards.
Also read: The Ultimate Guide To Manufacturing Translation
The main goal of this regulation is to protect human health and the environment by ensuring that chemical dangers are clearly communicated to workers and consumers across the EU member states.
Who and what does the CLP regulation apply to?
The CLP Regulation EC No 1272/2008 applies to a wide range of substances and mixtures that are manufactured, imported, or used within the European Union. Specifically, it covers:
1. Chemical Substances
The CLP regulation applies to pure chemicals, whether industrial chemicals, consumer chemicals, or those used in various manufacturing processes. This includes solvents, acids, and bases used in industrial operations and chemicals found in everyday household products. According to this regulation, any chemical that poses a hazard must be classified and labeled in accordance with the CLP framework.
2. Chemical Mixtures
Under CLP, those products that consist of a mixture of chemicals such as paints, detergents, etc need to be evaluated for their overall hazard profile, and labels must reflect the cumulative risks posed by the combination of substances. So manufacturers of mixtures must follow strict guidelines to classify the hazards correctly and communicate them on the packaging.
The CLP regulation also applies to anyone who produces, imports or uses hazardous substances or mixtures. This includes manufacturers of chemicals, companies that import chemicals from non-EU countries, and downstream users such as industrial facilities or smaller companies that use chemicals in their processes.
Even the repackagers and distributors in the EU region must also comply to these regulations.
Language and translation requirements as per the CLP Regulation EC No 1272/2008
A key component of the CLP Regulation EC No 1272/2008 is its focus on language and translation requirements to ensure the clear communication of chemical hazards across all EU member states.
This ensures that workers, transporters, and end-users are well-informed about the risks and safety measures associated with handling, transporting, or using chemical substances and mixtures
The CLP mandates that important documents and labels be translated into the country’s official language(s) where the chemical substance or mixture is being sold or used.
These include:
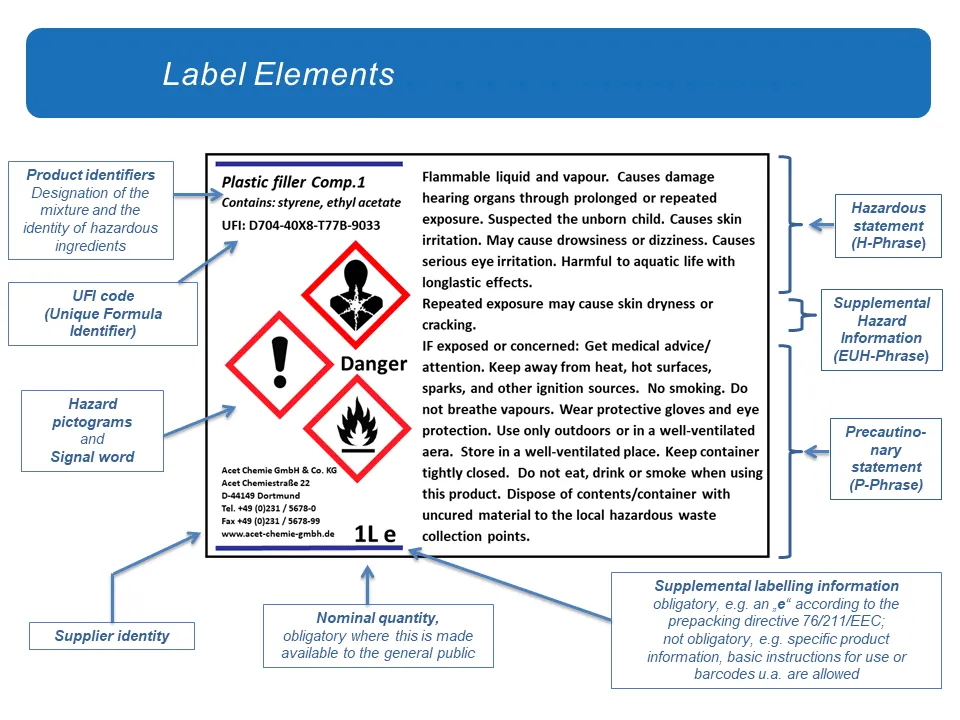
1. Labelling
According to Article 17 of the CLP regulation,
- The substance or mixture sold must have labels written in the official languages or the languages of the EU member states.
- Suppliers may use more languages on their labels than those required by the Member States, provided the same details appear in all languages used.
- All the information regarding hazard statements, precautionary statements, signal words, and pictograms must be translated.
- Although Article 17 allows the use of multiple languages, it is required that all the mandatory information should be presented in a way that does not confuse the users
- In “Switzerland and Luxembourg” the substance or mixture sold must have labels in at least two official languages or, with the agreement of the final users, it may be labelled in only one official language or in English.
By standardizing the language requirements across EU member states, Article 17 aims to create a consistent approach to chemical labelling, reducing confusion and enhancing safety across borders.
2. Safety Datasheets
According to Article 17 Annex 2 of the CLP regulation,
- Safety Data Sheets must be made available in the official language(s) of the member states where the product is placed in the market
- Detailed information about the chemical substance or mixture, including hazards, handling instructions, storage guidelines, and emergency measures must be translated and provided in all the official languages of the member states.
- In Switzerland and Luxembourg, the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) should be available in the official languages preferred by the customer or in another language agreed upon by both parties, with the annex of the SDS may be written in English.
Who is responsible for the CLP regulation translation?
Under the CLP Regulation, the party responsible for placing a chemical substance or mixture on the EU market is typically responsible for the translations
They include:
Manufacturers,
Distributor, or
Importer,
If a user imports/uses a chemical product with labels or Safety Data Sheets (SDS) that are not translated, they can arrange for the translation. However, the manufacturer is still responsible for ensuring the accuracy of these translations to make sure that all safety information is communicated correctly
Languages to be translated to
The CLP regulation requires that translations be made into the official language(s) of the member state where the chemical substance or mixture is being marketed or used.
Here is the list of all the languages required for labels and safety data sheets in the EU market

This means that if a chemical substance or mixture is intended for multiple countries within the EU, must be translated into the respective official languages of each country.
In practice, this can require translating labels and SDS into more than 20 languages, depending on the target markets
Translations in compliance with the CLP Regulation
Milestone works with native translators with domain expertise to accurately translate your documents into 70+ languages. We provide translation certificates accepted by authorities across the globe.
Challenges of CLP Compliance in Multiple Languages
Challenges Faced During Translation in Terms of the CLP Regulation
The CLP Regulation (Classification, Labelling, and Packaging of Substances and Mixtures) presents several challenges when it comes to translation, especially for companies dealing with hazardous chemicals across various countries in the European Economic Area (EEA).
1. Language Variability
The CLP Regulation requires that labels and Safety Data Sheets (SDS) be provided in the official language(s) of the member state where the product is marketed. This can be challenging when a product is sold in multiple countries, as suppliers must ensure that all required information is accurately translated into different languages while maintaining consistency across versions
2. Complexity of Chemical Terminology
Chemical names, hazard statements, and precautionary measures often contain specialized terminology that may not have direct translations in other languages. This complexity necessitates the use of professional translators with expertise in chemical safety to ensure accuracy
3. Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring compliance with both the CLP Regulation and local regulations can be difficult. Some member states may have additional requirements regarding language use on labels and SDS, which must be adhered to alongside EU-wide regulations
4. Maintaining Clarity and Readability
With multiple languages on a single label, maintaining clarity and readability is crucial. The CLP allows for multi-language labels but requires that all information be grouped logically. This can complicate design and layout efforts, especially for products with extensive hazard information.
5. Changing Regulations
The CLP Regulation is regularly updated and revised, making the translation process more complex Companies must stay updated on these changes to ensure their labels comply with the latest regulations. This involves understanding the implications of new hazard classifications on labelling requirements.
6. Inconsistent Information Across Documents
There is often a risk that the information presented on labels may not match what is provided in the SDS due to translation errors or oversight during updates. This inconsistency can lead to confusion among users regarding safety measures and hazards associated with a chemical product
7. Resource Availability
“Finding reliable resources for translating specific chemical terms or obtaining substance names in different languages can be challenging. While some resources exist (e.g., ECHA’s database), they may not cover all substances or provide comprehensive translations”.
Also read: A Comprehensive Guide To Navigate Technical Translation
Best Practices for CLP Regulation Translation

To ensure compliance with the CLP Regulation and to facilitate the safe handling and communication of hazardous chemicals, companies should adhere to several best practices for translation:
1. Native-Speaking Translators with Industry Expertise
Work with a translation agency that has native-speaking translators with expertise in chemical safety and regulatory compliance to ensure that the translations are technically accurate and reflect the correct terminology used in the original documents.
2. Work with ISO-Certified Translation Companies
Work with ISO-certified translation companies that adhere to standards like ISO 17100 and ISO 9001. These companies follow strict quality control protocols and employ qualified translators, ensuring the highest standards for accuracy and consistency.
3. Support for Label Formatting and Design
CLP regulation translations often include chemical documents like labels and safety sheets with specific formatting and layout requirements. They may contain hazard pictograms and multilingual text. Confirm that the translation agency offers formatting and desktop publishing (DTP) services to ensure that your translated content fits perfectly within the design parameters of labels, safety data sheets (SDS), and other regulatory documents. This ensures that the final output is fully compliant and ready for use.
4. Rigorous Quality Control Processes
A reliable translation agency should have a comprehensive quality assurance (QA) process, which includes multiple layers of review such as proofreading, editing, and technical checks. This ensures that the translations meet all regulatory requirements and are free of errors.
5. Use of tools and technologies
Ask about the tools and technologies the provider uses to enhance accuracy and consistency. Top companies rely on resources like translation style guides, terminology databases, translation memory, and computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools to ensure that standardized CLP terms, such as hazard and precautionary statements, are translated uniformly. These tools also help minimize errors and improve translation efficiency.
6. Compliance with GHS
According to the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), hazard classes, signal words, pictograms, hazard statements, and precautionary measures should be communicated to its users in all official languages of the countries where the product is sold or marketed. Translators must use standardized phrases and terms outlined in the regulation to maintain this consistency.
Conclusion
Compliance with the CLP Regulation EC No 1272/2008 is essential for companies in the chemical industry looking to expand into global markets. Adhering to this regulation helps ensure the safety, effectiveness, and accuracy of hazard communication related to chemical substances and mixtures.
The regulation mandates that essential documentation, such as Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and labels, must be translated into the official languages of the EU member states where these chemicals are distributed or utilized.
By fulfilling these language requirements and implementing best practices for translation, manufacturers not only meet their regulatory obligations but also enhance safety for end-users and streamline their market entry process throughout Europe.
Also read: EU Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC: Translation Requirements
Looking for Chemical Translation services ?
Milestone works with native translators with domain expertise to accurately translate your documents into 70+ languages. We provide translation certificates accepted by authorities across the globe.