South Asia is a vast region that consists of Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka. Afghanistan and Maldives are often considered a part of South Asia as well.
This region is often referred to as the Indian subcontinent since it is located on the Indo-Gangetic Plain and peninsular India. However, this term more frequently used to denote the group of Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan.
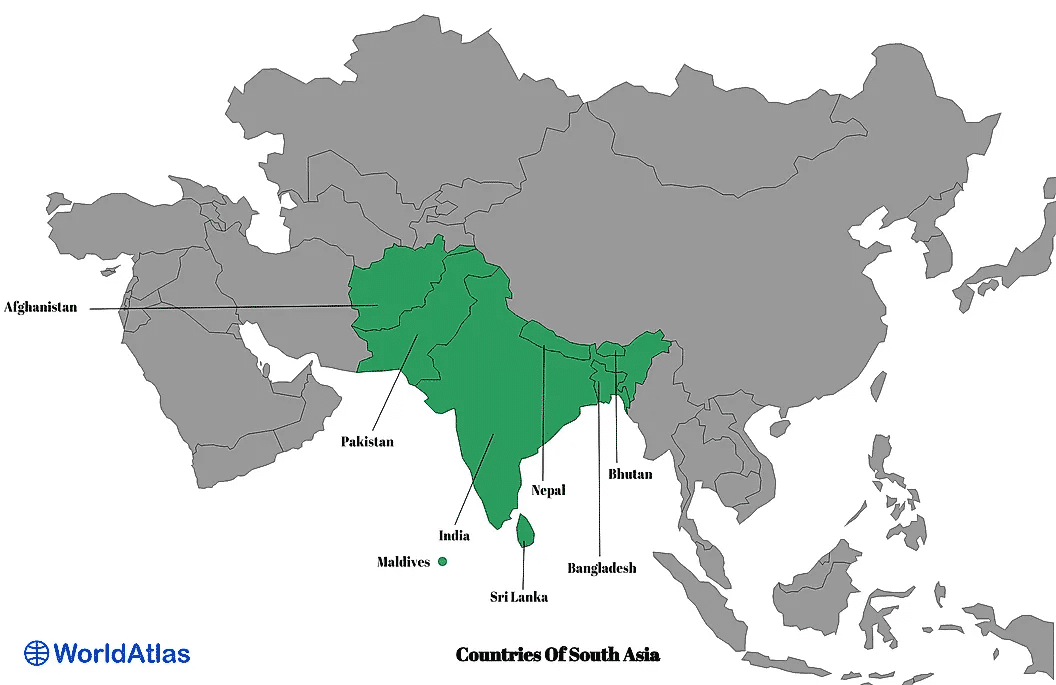
This area one of the most diverse regions in the world – both linguistically and culturally. South Asia is home to one of the earliest civilizations that the world has ever known – the Indus Valley civilization.
Today, South Asia is among the most densely populated regions in the world. In fact, nearly 1.9 billion people live in this region where one-fourth of the world’s population.
On its territory spoke hundreds of different languages and dialects. Some of them spoken by millions whereas others have just a few thousand speakers left.
While some languages of South Asia are disappearing, others like Hindi, Punjabi, Bengali, and Marathi are among the top 10 fastest growing languages in the world.
The languages of South Asia are gaining more and more popularity and in the next decades they will most likely take over the world. If you want to learn more about this region and its linguistic heritage, sit back and enjoy our blog about what languages are spoken in South Asia and Most Spoken Languages of South Asia.
1. History and multilingualism of South Asia
A few decades ago South Asia did not exist in the regional sense we know it today. The countries of this geographical area define the British Raj.
In other words, the region ruled by the British Crown and was often referred to as the Indian Empire.
The territory of the British Raj or India covered more or less the territory of the whole region of South Asia. What’s more, in a formal sense, India was not exactly a colony, but rather a separate state which shared a Monarch with Britain.
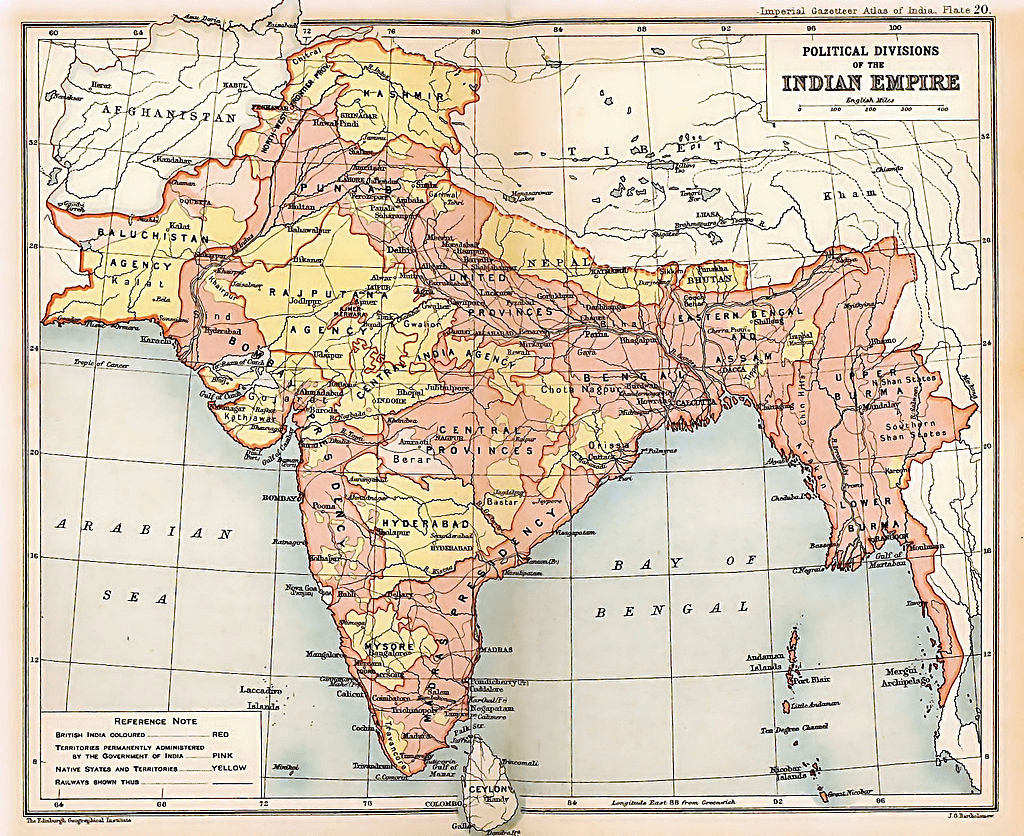
After the end of British rule in 1947, the so-called Indian Empire got divided, and other countries emerged. Initially, India and Pakistan recognized as independent states. Later on, in 1971 the People’s Republic of Bangladesh was established.
Also Read: Languages of East Asia [Complete Guide]
Despite the colonization of the region, South Asia has kept its linguistic and cultural diversity.
Although the countries of this region remained under British rule for over a century, it would be virtually impossible to define a national language or national literature of the region since this area is so diverse.
However, one should also think about the consequences of so many languages being spoken in one place. How do people communicate with each other when they have different native languages?
The multilingual population of South Asia
Indeed, multilingualism is very common in this region. And while multilingualism is a sign of prestige in Europe, in South Asia the reason for people to be bi- or trilingual is more practical – communication.
The multilingual population of South Asia is the subject of studies for many linguists. What’s more, code-switching or the use of words and phrases from one language into their main language can be frequently observed in this multilingual region.
Linguists have observed how different languages are allocated to particular domains and there are no bilingual institutions or certain overlaps between the spheres.
For instance, humanitarian subjects are generally taught in the indigenous languages of the region while science, technology, and math in English.
Nevertheless, despite the heavy influence of English, Hindi, Punjabi, Bengali, and Marathi remain among the top 10 fastest-growing languages in the world.
Also Read: Hinglish- A Report on Usage and Popularity in India
2. The writing systems of the South Asian languages
According to archeological evidence, the first written language in India dates back to the third millennium B.C.E.
However, the ancestor of most of today’s Indian scripts, Brahmi, appeared in the third century B.C.E. Later on, it developed into the script of the Devanagari writing system and influenced the script of the Dravidian language family.
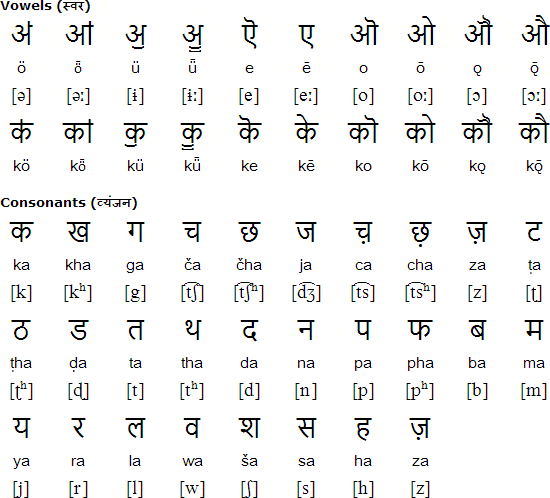
Islam and its holy book the Quran brought about the Arabic script which heavily influenced the Urdu writing system.
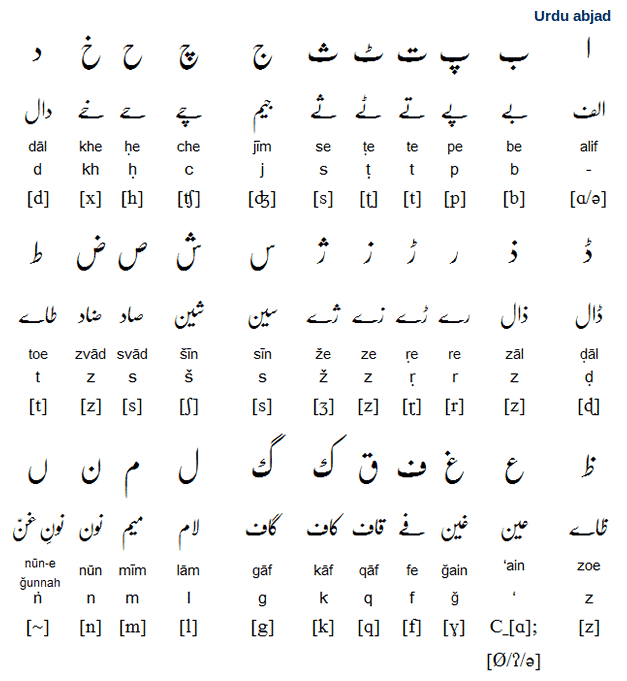
Lastly, European colonialism and more particularly, the establishment of English led to the adaptation of the Latin script.
Also Read: Hindi vs Urdu: What’s The Difference?
Since the Roman script has less complex characters and is considerably more widely distributed, many publishers were pressed to transliterate the Indian languages into the Latin script.
3. The language families of the languages of South Asia
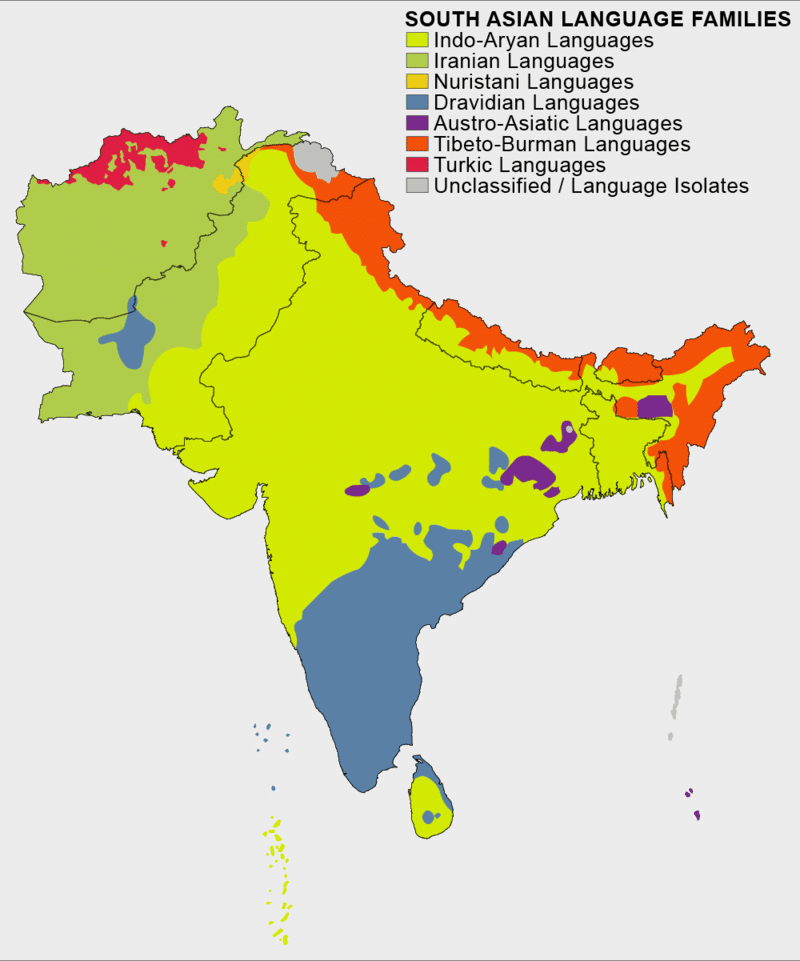
Generally, there are two main language families in South Asia. Of course, there are numerous other language families, however, their languages are not as widely distributed in South Asia.
Moreover, there are tribal languages and dialects which, however, do not belong to any language family (for more information have a look at the map below).
- The Indo-Iranian languages are mostly spoken in northern and western India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal as well as southern and western Sri Lanka.
Some languages that belong to this group are: Hindi, Gujarati, Bengali, Assamese, Baluchi, Nepali, Oriya, Panjabi, Pashto, Sanskrit, Sindhi, Sinhala, and Urdu.
The Dravidian languages –predominantly spoken in southern India as well as northern and eastern Sri Lanka. Some examples are Kannada, Malayalam, Telugu, Tamil.
4. Languages of South Asia
Thousands of languages spoken in this region, however, it would be hardly possible to summarize all of them.
This is why in this section we have selected the most widely spoken ones.
- The Hindustani language is the lingua franca of Northern India and Pakistan. This is a pluricentric language. This means that it has several standardized forms. In the case of the Hindustani language, there are two standardized registers.
- Hindi or Modern Standard Hindi language is spoken mainly in India. It has nearly 530 million native speakers in India, nearly 140 million L2 speakers, and approximately 25 million L3 speakers. This the 3rd most spoken language in the world.
- The Urdu language is the official language of Pakistan and recognized by the Constitution of India and thus, has an official language in some Indian states. It has nearly 230 million speakers which makes it the 10th most spoken language in the world.
Other Popular South Asian Languages
- Bengali (also called Bangla) is the lingua franca of the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent. The most spoken language in Bangladesh and in India, after Hindi. It has 228 million L1 speakers and 37 million L2 speakers. It is the fifth most spoken native language and the sixth most spoken language in terms of the total number of speakers in the world. Nearly 98% of the population of Bangladesh speak Bengali. The language estimated to be 1,300 years old.
- Tamil is an official language in India and Sri Lanka. Predominantly spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. It has 75 million native speakers and 8 million L2 speakers.
- Telugu has primarily spoken by the Telugu people in some Indian states. It has one of the highest numbers of native speakers in India – 84 million people. Around 11 million people speak it as an L2.
- Marathi spoken by the Marathi people from the Indian state of Maharashtra. This is the 15th most widely spoken language in the world with 84 million speakers and 12 million L2 speakers.
- Gujarati has official status in some Indian states. Moreover, it is the 6th most widely spoken language in India with 56 million native and 4 million L2 speakers10.
- Punjabi spoken by the Punjabi people in the Punjab region of India and in Pakistan. It has approximately 113 million speakers and more than 80 million of them are in Pakistan. Yet, it has no official status there despite being the most widely spoken language in the country.
- English is commonly used in urban areas and is a major economic lingua franca of South Asia. English was introduced and reinforced by the British Empire in the 17th century.
5. The English language in South Asia
English is among the most frequently spoken languages in this region – it is an official language in India, Pakistan, and the Maldives.
Moreover, English is the main medium of instruction in both public and private schools in quite a few Indian states.
In Pakistan and Bangladesh English is an obligatory subject at all educational institutions such as schools, colleges, and universities.
In fact, India is in the top 3 countries with the biggest English-speaking populations (only behind the USA) followed by Pakistan.
Table 12 below gives a more in-depth overview of the English-speaking population in the region.

It should also points out that there are several South Asian English subvarieties such as Bangladeshi, Indian, Pakistani, Nepali, and Sri Lankan English.
They have only very few differences between each other and thus, they are to a great extent mutually intelligible.
What’s more, their differences are mainly in terms of vocabulary and pronunciation since it is adapted to the local language.
South Asia also publishes more literature in English than any other part of the world outside of the UK and North America. This clearly shows the status that the English language has in this region.
Also read: Top 10 Translation Companies In Bangalore
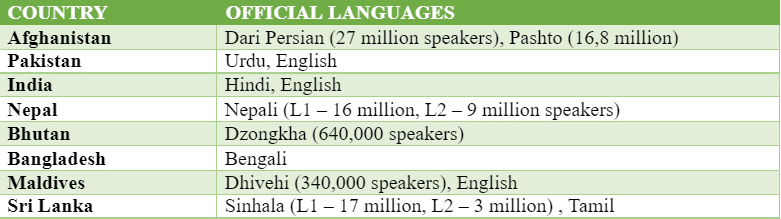
6. Official languages of the countries of South Asia
Despite this incredible linguistic diversity, only a few of the languages of South Asia are recognized as official languages in the countries of the region.
The following table presents a more thorough overview of the official languages in South Asian countries.
To Conclude
Without a doubt, the linguistic diversity of South Asia is one of a kind! What’s even more fascinating is the fact that all these languages have survived despite the century-long British rule.
Today English has adapted to the indigenous languages of South Asia and they co-exist in harmony.
Moreover, owing to the population and growth of the region, it seems like the Hindi language, Punjabi, Bengali, and Marathi have the potential to even surpass the popularity of the English language in the decades to come.
Also read: Top 10 Translation Companies in India 2024