Many people are rather confused when it comes to the Slavic languages. Everybody has heard of Russian, Polish, Czech, Ukrainian, Belarusian, Bulgarian, Slovak, etc., but not many people actually know that these are all actually Slavic languages.
They are distributed primarily in eastern Europe and thus, many people outside the continent are not familiar with them.
Slavic languages have a long and rich history. They unite huge parts of Europe such as the Balkans as well as Central and Eastern Europe.
What’s more, they are such a diverse group of languages that it is definitely worth getting to know them a bit more!
In this blog, we are going to talk all about the list of Slavic languages, their history, how they differ from one another, and how are they similar.
1. What are Slavic languages? What is the history of Slavic Languages?
The Slavic languages form a group of languages spoken by nearly 400 million people in Europe and Northern Asia.
These languages developed from the Proto-Slavic language, which itself stems from Proto-Indo-European. The origin of Proto-Slavic is believed to be between the Dnipro River and the Oder River.
This was the language spoken by all Slavs or Slavic people between the 8th and 9th century A.D.
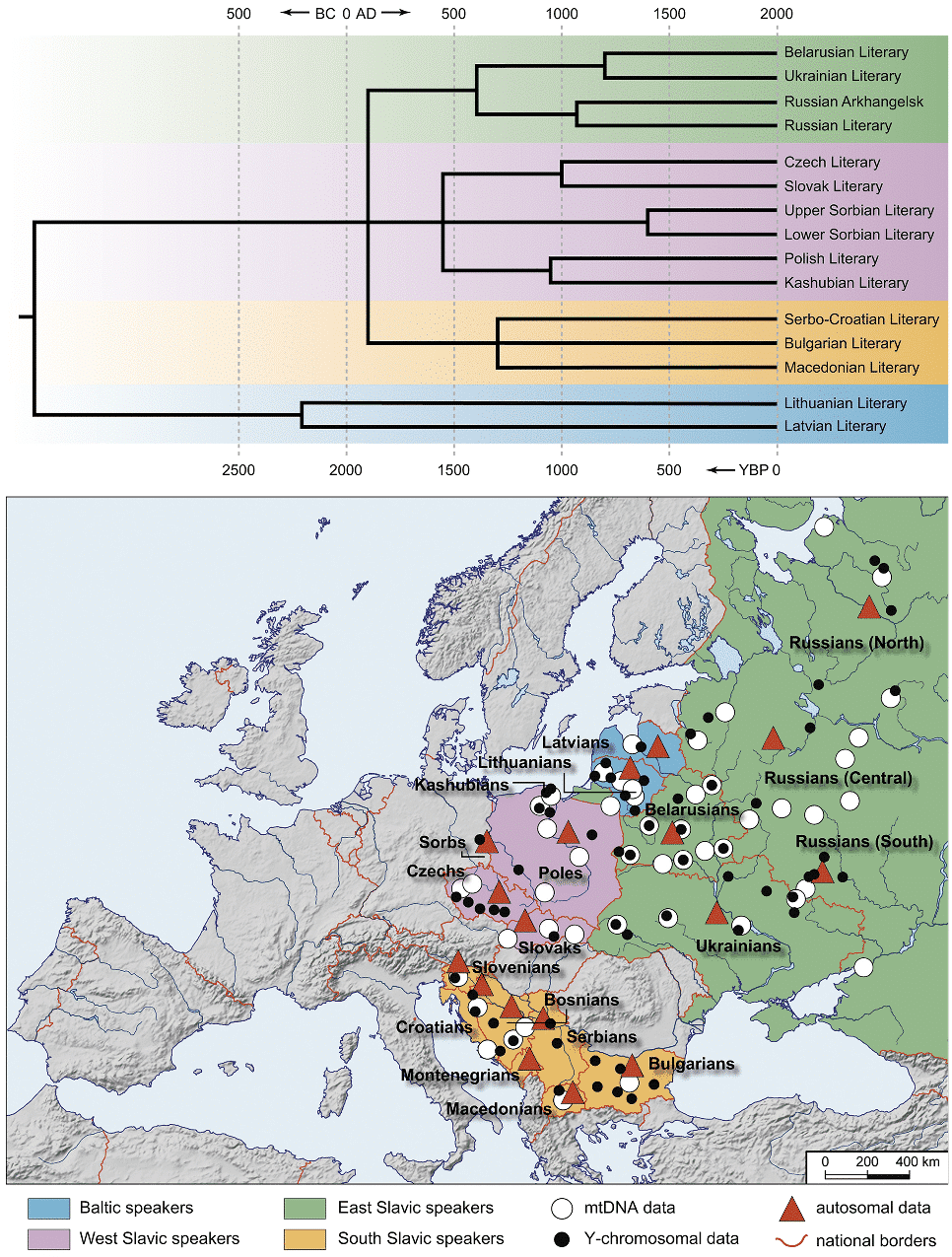
Through the centuries separate languages emerged which developed independently from one another.
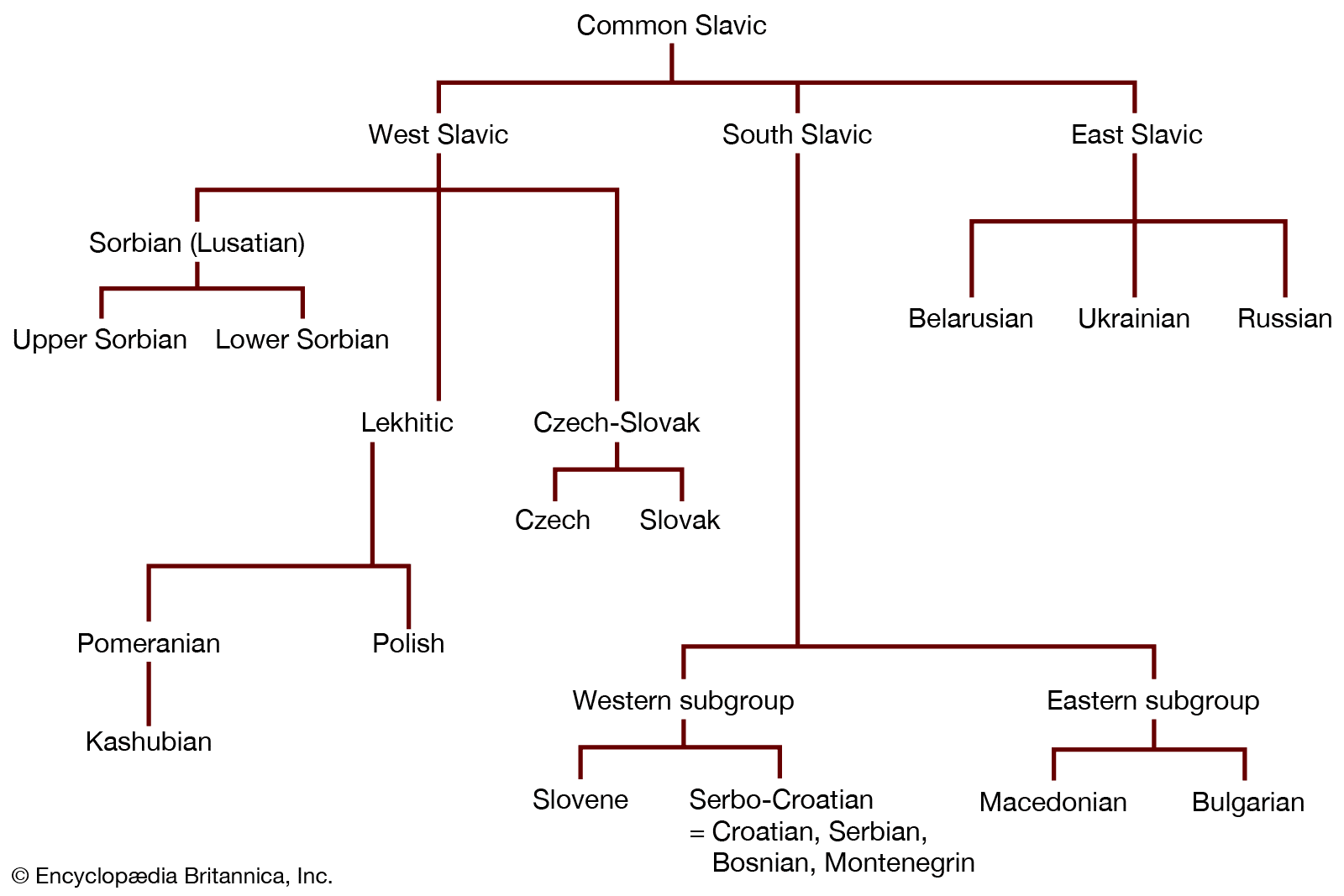
Today there are 12 Slavic languages. Interestingly, there is also one Slavic language that has become extinct – Polabian.
These 12 Slavic languages can be divided into three main categories – East, West, and South or North, Central, and South. The latter being less accepted.
This division is based entirely on the geographical location of each language and has nothing to do with their historical or linguistic development.
Moreover, these languages, despite their common origin, have very few similarities.
2. What are the Slavic languages?
As pointed out above, Slavic languages can be divided into three categories, depending on their geographical location.
In this section, we will look into all 12 Slavic languages and discuss their most prominent features.
Eastern Slavic Languages
Let’s start off with Russian, Ukrainian, and Belarusian. They belong to the East Slavic language group and presumably, due to their close locations and common history, share a lot of similarities.
Hence, many of their speakers can communicate with each other rather easily.
- Russian
Russian is the most popular Slavic language and the most widely spoken one. Nearly 150 million people in Russia speak this language, however, the total number of Russian speakers around the world is almost double – 270 million people.
Indeed, Russian is one of the most spoken languages not only in Europe but in the world as well.
Also Read: 7 Common Russian Translation Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Russian is one of the few Slavic languages, which uses the Cyrillic alphabet. In addition, it has a complex case system, consisting of 7 cases.

- Ukrainian
Many people think that Ukrainian is simply a Russian dialect, however, this is completely wrong. Ukrainian is a separate language that has some similarities with Russian.
There are more than 30 million speakers in Ukraine and an additional 2 million Ukrainian speakers around the globe. Besides Russian, Ukrainian is also very similar to Belarusian.
Interestingly, Ukrainian has had a great influence on Polish, which has resulted in some common vocabulary.
- Belarusian
Belarusian is spoken by fairly few people around the world – nearly 2.5 million speakers and 2 million of them live in Belarus, although the country is home to over 9 million people.
Many Belarusian people can speak only Russian.
The two languages share a lot of similar grammatical features and vocabulary and thus, they are fairly mutually intelligible.
This is why communication between the speakers of the two languages is pretty smooth.
Belarusian, despite its low number of speakers, has three major dialects: Southwest, Northern and Central Belarusian. Similarly, to Russian, Belarusian uses the Cyrillic alphabet.
Western Slavic Languages
Moving on to the group of West Slavic languages which consists of 3 languages: Czech, Slovak, and Polish.
Some linguist includes also Lower and Upper Sorbian and Kashubian in this group. However, these languages are spoken by very few people nowadays and are believed to become extinct in the near future.
- Polish
Polish is the most widely spoken language from this group. It is spoken by 40 million people and most of them are in Poland.
More specifically, Polish belongs to the Lechitic language family. This subgroup of languages includes Polish, Kashubian, Slovincian (an archaic variety of Kashubian), and Polabian which no longer exists.
Polish does not use the Cyrillic, but the Latin alphabet.
Also read: What Are The Fastest Growing Languages?
- Czech
Czech is considerably less popular than Polish with its 13 million speakers. It also uses the Latin alphabet and is notorious for having one of the hardest case systems of all Slavic languages.

- Slovak
Slovak and Czech are closely related languages and thus, the communication between their speakers is rather unproblematic.
The Slovak is less spoken than Czech – only 5 million speakers live in Slovakia and 2 million speakers live abroad. Again, Slovak speakers write with Latin letters.
- Lower Sorbian and Upper Sorbian
Sorbian, also known as Wendisch, is spoken by around 55,000 people in the areas of Saxony and Brandenburg, Germany.
The language emerged around the 16th century. There are two varieties of Sorbian – Upper, based on a dialect spoken in Upper Lusatia, and Lower, originating from the Cottbus dialect which was spoken in Lower Lusatia.
In the 19th century, both of these varieties became a standard language in their respective region.
Since then Sorbian is thought at school, there are a few papers and magazines in Sorbian and up to 10 hours of Sorbian programmers are broadcasted weekly on the German television and radio.
Also read: German vs Russian: Which Language Has A Brighter Future?
- Kashubian.
Kashubian is spoken by 200,000 people, but only one-fourth of them use it on a daily basis. Kashubian speakers inhabit the North and Central part of Poland.
Interestingly, there are Kashubian speakers in Canada as well. Until very recently it was considered to be a Polish dialect.
The earliest examples of Kashubian literature date back to the 16th century A.D. Today only a few schools exist where Kashubian is taught.
Get in touch for Slavic Language Translations
Milestone helps you seamlessly translate content & localize your website, products, and services for more reach, better conversions, and greater sales.
South Slavic Languages
Finally, we are coming to the South Slavic languages which are distributed across the Balkans and parts of Central Europe. This group is very diverse and still quite similar.
- Bulgarian
Around 7 million speakers live in Bulgaria and nearly 2 million native Bulgarians are scattered around the world.

Similar to the languages from the East Slavic group, Bulgarian speakers write in the Cyrillic script.
Moreover, although Bulgarian does have a case system, it’s not as complex since many of the endings are identical.
A fun fact about Bulgarian is that the verbs have no infinitive form.
Also Read: Business in Bulgaria – Why Move your business to Bulgaria?
- Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin
It should be pointed out that these are four separate languages, however, they share so many similarities that one could mistake them for the same one.
They are also known as Serbo-Croatian – this is a pluricentric language consisting of four mutually intelligible standard varieties – Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin.
Some linguists believe these are dialects of the same language and their divided due to political reasons.
Overall, these languages are spoken by around 15 million people. An important difference is that Serbian and Montenegrin use both the Cyrillic and the Latin alphabet, while Croatian and Bosnian only the latter.
- Slovene
Slovene, also referred to as Slovenian, is spoken by only 2 million people and is one of the youngest Slavic languages. Still, it has a wide range of dialects.
Moreover, its difficult pronunciation and complex grammar are what sets it apart from the other Slavic languages
Also read: 10 Untranslatable Bulgarian Expressions
3. Similarities and differences between Slavic languages
All these languages stem from the Proto-Slavic languages and thus, share a lot of common features in terms of grammar and vocabulary.
This rather big group of 12 languages, however, is characterized by a great variety. All these languages used to be dialects of Proto-Slavic.
Still, as they continued to develop through the centuries, more and more differences started to emerge between them.
Differences between the Slavic Languages
Overall, it can be claimed that Slavic languages differ primarily in terms of:
- Use of Latin or Cyrillic alphabet
- The complexity of the case system (most Slavic languages have 7 cases, but the endings denoting these cases have become more or less obscure in some Slavic languages, e.g. Bulgarian)
- Pronunciation (e.g. different degree of palatalization – if we compare Russian and Bulgarian, Russian sounds “softer” due to palatalization processes it has undergone)
- Vocabulary (see the table below)
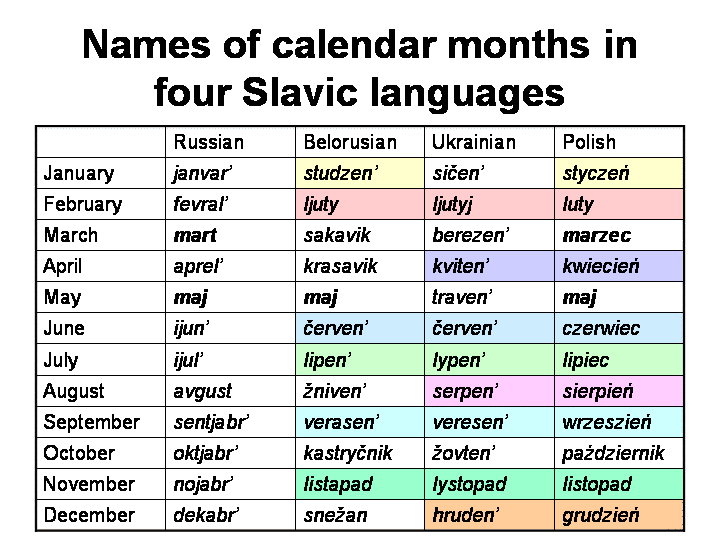
Similarities between Slavic languages
Nevertheless, as a group of languages with a common origin, there are undoubtedly a number of similar features such as:
- Inflection (e.g. the use of suffixes to mark tenses, cases, etc.)
- Endings are widely identical (e.g. -те denotes second person singular and third-person plural)
- Verb aspect (the verb form expresses whether the action is completed or ongoing; e.g. in Russian заходить means “to start walking” while ходить is the continuous act of walking)
- Three main genders of nouns and pronouns (masculine, feminine and neutral)
- Flexible word order (due to the existence of so many cases)
Also read: Bulgarian vs Russian: Difference and Similarities
4. Is Russian a Slavic language?
Is Russian a Slavic language? Yes, it is!
It is the most widely distributed Slavic language with over 400 million speakers in Russia, Asia, and, more or less, all over the world.

Probably the most prominent feature of Russian, which also indicates it is nothing else, but a Slavic language, is the fact that Russian uses the Cyrillic alphabet.
This writing system is predominantly used by Slavic languages.
What’s more, Russian shares a lot of grammatical features with the other Slavic languages such as the complex cases system, for instance.
Also read: 10 Facts You Never Knew About the Russian Language
But most importantly, as you can see on the chart, Russian shares a common ancestor – the Proto-Slavic language – with all other Slavic languages.
Having a common origin is, indeed, the pre-eminent feature that renders Russian a Slavic language.
To Conclude
All in all, all Slavic languages form a diverse family. Although these languages are predominantly spoken in Europe, they are distributed over the whole continent which, in turn, offers you a great opportunity to expand to new markets.
The Balkans, as well as Eastern Europe, are rapidly developing markets and can provide you with profitable opportunities for your business.
Also read: Top 6 Languages For Your Business
Get in touch for Slavic Language Translations
Milestone helps you seamlessly translate content & localize your website, products, and services for more reach, better conversions, and greater sales.




