India introduced the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) in 2023 to address the need for comprehensive data protection laws. This act is a significant move towards regulating the collection, processing, and usage of digital personal data within the country’s borders.
In this blog, we will delve into the details of the DPDPA, explore the importance of language services for compliance with the law, and discuss the process of translating relevant documents.
Are you looking for DPDPA compliant translations?
Our native translators with legal expertise can accurately translate your requests, notices, and other relevant documents into all 22 official Indian languages.
What is the Digital Personal Data Protection Act?
In August 2023, India passed the Digital Personal Data Protection Act to regulate the use of digital personal data. The law aims to balance the right of individuals to protect their personal data with the need to process such data for legal purposes and related matters.
The DPDPA aims to preserve individuals’ control over their personal data through a set of rights for data principals and duties for data fiduciaries. These rights include the access, correction, and deletion of personal data.
As per the act,
Data Fiduciaries refer to any person or group of persons who, alone or in combination with others, decide on the purpose and method of processing personal data.
Data Principals refer to individuals whose personal data is being processed. If the individual in question is a child, their parents or lawful guardian are considered data principals.
Similarly, if the individual is a person with a disability, their lawful guardian acting on their behalf is also considered a data principal.

Which organizations does India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act apply to?
This law applies to all businesses irrespective of their place of operation if they offer goods or services to individuals and data principals in India. The provisions of this act apply to the processing of digital personal data if:
- The personal data is collected online or in digital form
- The personal data are collected offline or in non-digital form and then digitized.
The Act doesn’t apply to personal information that an individual processes for personal use.
The Act also doesn’t apply to personal information that an individual or someone else makes publicly available if they are required to do so by law in India.
Also read: User Agreement Translation: Why Should Companies Do It?
The effective date of the DPDP Act
The DPDP Bill was passed by both houses of Parliament in August 2023. In January 2025, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) released the Draft Digital Personal Data Protection Rules, 2025 for public consultation.
Implementation will be phased, with provisions related to the Data Protection Board coming into effect immediately upon final notification, while compliance requirements for businesses are expected to be implemented by mid-2025. Reports suggest businesses may have a two-year transition period to achieve full compliance.
Once the implementing rules are notified, a 45-day consultation period will follow, leading to the establishment of the Data Protection Board (DPB).
Large IT companies and affiliated businesses are advocating for a two-year transition period to comply with the DPDP Act.
Language requirements as per the DPDP act
As per the DPDP act, The Data Fiduciary, who is responsible for handling personal data, must provide the Data Principal with the option to access notices and requests in either English or any language specified in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution.
This ensures that individuals can understand the information presented to them in a language they are comfortable with or proficient in.
When seeking consent from the Data Principal, the request must be presented in clear and plain language, and the individual must again be given the choice to access the request in English or any language specified in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution.
The 22 languages specified in the Eight Schedule of the constitution are Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, and Urdu. 
Need for Translation in achieving compliance with the DPDP act
To comply with data protection laws, it is essential to take a holistic approach that emphasizes clear communication, especially in languages that Data Principals can understand. The law mandates Data Fiduciaries to offer notices and requests to Data Principals in English or the 22 languages recognized in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution.
Translation services are crucial for complying with the language requirements of the DPDP Act. This is further emphasized in the Draft Digital Personal Data Protection Rules, 2025, which specify that notices must be presented in ‘clear and plain language’ and should be ‘standalone and self-explanatory.’ Properly translated notices and consent requests ensure Data Principals can understand their rights and make informed decisions about their personal data.
Additionally, by providing information and consent requests in multiple languages, businesses can empower individuals to understand their rights and obligations concerning personal data.
This can help build trust and foster transparency in the data collection and processing activities of businesses.
Also read: Legal Translation : Importance, Challenges & Best Practices
How to get started with the translation process to comply with DPDPA?
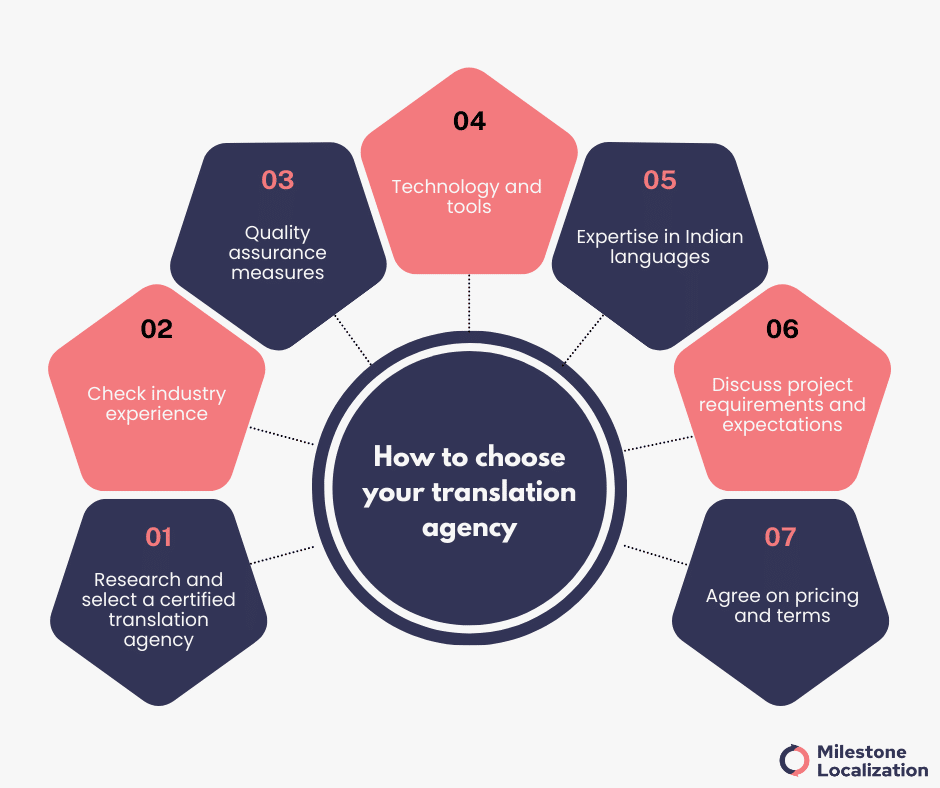
1. Research and Select a Certified Translation Agency
Look for reputable translation agencies such as ISO 17100: 2015 certified agencies, that offer certified translation services. These agencies have strong processes and systems in place to ensure high quality and accuracy.
Additionally, the ISO 17100:2015 certificate is specific to translation services.
2. Check Industry Experience
Verify that the translation agency has experience in translating legal and other related documents. Legal translation requires specialized knowledge of legal terminology, concepts, and conventions. Look for agencies that have a dedicated team of legal translators or specialize in legal translations.
3. Quality Assurance Measures
Inquire about the agency’s quality assurance processes. The agency should have stringent quality control measures in place to ensure accurate and error-free translations. This includes translations by native translators, proofreading, editing, quality checks, and adherence to industry standards such as ISO 17100.
4. Tools and technology
Choose an agency that utilizes advanced translation technology and tools such as translation memory, terminology database, etc., to streamline the translation process and maintain consistency.
These tools can help improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure consistency across translations.
5. Expertise in Indian Languages
Since the DPDPA requires the notices and consent requests to be in English & the 22 official languages of India, ensure that the agency is well-equipped with native translators who have expertise in all these languages.
6. Discuss Project Requirements and Expectations
Communicate your project requirements and expectations in detail to your language service provider. Provide clear instructions, timelines, and any specific preferences or guidelines for the translations.
Communication is key to ensuring that the agency understands your needs and delivers translations that meet your expectations.
7. Agree on Pricing and Terms
Clarify the pricing structure, payment terms, and any additional services or fees associated with the translation project. Make sure you have a written agreement or contract that outlines all terms and conditions to avoid any misunderstandings later on.
Also read: Legal Translation – 6 Practical Tips for Translating Legal Documents
GET your documents translated by professional legal translators
Our team of expert native translators with legal expertise can translate your notices, requests, and other relevant documents in all 22 official Indian languages to ensure DPDPA compliance.
Factors affecting the cost of translation

Language pair: Prices differ for each language pair based on the number of speakers, the demand, and the supply of qualified translators of that language.
Volume and complexity: More complex texts like technical, medical, and legal documents, etc., require in-country specialists with significant experience, education, and certifications, which makes their translation more expensive.
To comply with the language requirements of the DPDPA, it is best if a native translator with legal expertise works on the translations. However, this will be in a higher price range compared to general content translation since it requires expertise.
Urgency: The shorter the deadline, the higher the price. So, if you want to save money, plan for your translation project and start earlier so that you have enough time for any revisions and comply with the regulations on time.
Quality assurance: Depending on the purpose, and the quality requirements of your translation project, you can opt for Translation (T) or Translation and Proofreading (T+P).
Since the accuracy is higher in the latter, the price is also higher. For legal translations and for documents that require utmost accuracy, it is always recommended to opt for T+P to ensure quality output.
Length: The most common way to calculate the price of a translation project is with its word count. Each translation agency has its rates per word for each language, so simply multiply the number of words in your document by the given rate.
Translation process at Milestone Localization
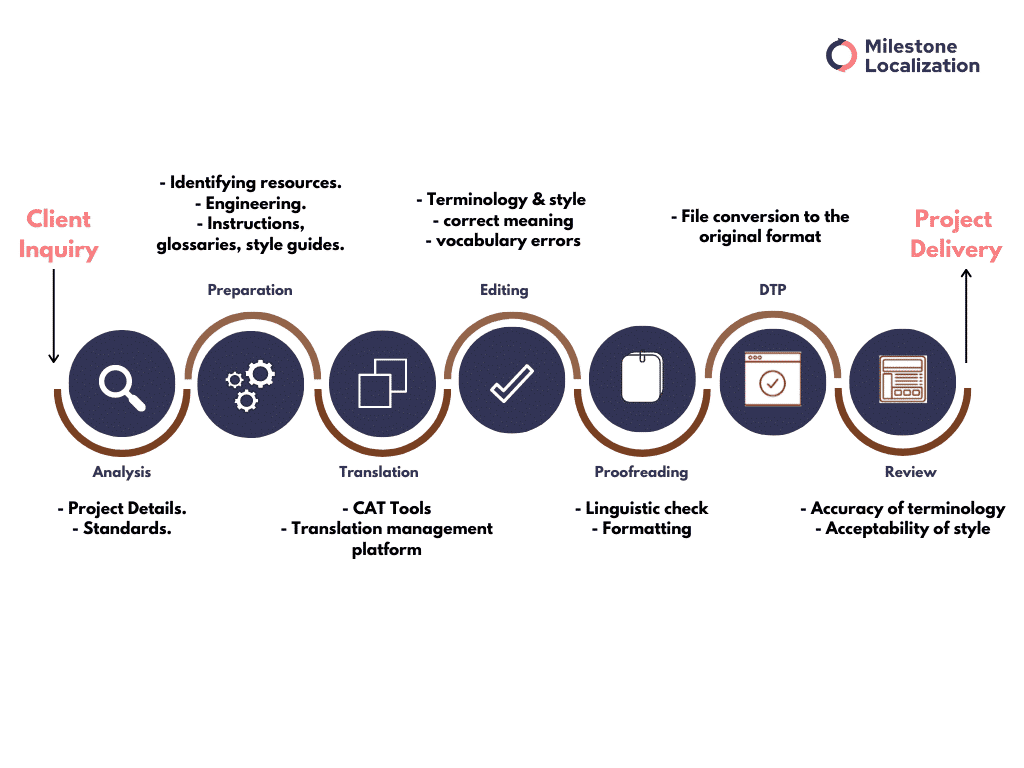
1. Understanding the Project Scope
To begin the translation process, the team assesses the project’s scope, objectives, deadlines, file formats, and client goals. They work closely with the client to get a thorough understanding of the project and desired outcomes.
This helps develop a tailored project flow that addresses the unique challenges and requirements of the project.
2. Initiating the Project
After the scope of the project is set in place, the team initiates the translation process by establishing clear communication channels and project milestones. A detailed project plan is prepared, outlining key deliverables, timelines, and quality benchmarks.
Additionally, a custom translation style guide and glossary are developed to ensure consistency in terminology and tone across all translated materials.
3. Team of Expert Linguists
Native linguists are carefully handpicked by your dedicated project manager considering the requirements of the project. The translators who work on DPDPA-related translations are legal experts with a minimum of 5 years of translation experience in the same.
They will undertake the translation and proofreading process as per the direction of the project manager.
4. Internal Quality Assurance
At every stage of the translation process, from initial translation to final proofreading, quality is given the utmost priority. All the translated content is proofread and edited by another expert legal translator to check for any errors and inconsistencies.
The proofread document goes through quality analysis and is checked against a comprehensive quality assurance checklist, covering factors such as terminology accuracy, grammar, style adherence, and contextual relevance.
5. Delivery and Review
Upon completion of the translation and quality assurance process, the translated files are delivered to the client for review and feedback.
Any feedback provided by the client is carefully analyzed and integrated into the translated materials, ensuring that the final deliverables align seamlessly with the client’s expectations and requirements.
Conclusion
The Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) is a significant step towards data privacy and protection in India’s digital landscape.
To comply with this, it’s essential to address the linguistic requirements mentioned in the act. Clear and accurate communication in languages understood by data principals is crucial and Language services, such as translation and localization, play a pivotal role in bridging the linguistic gap and facilitating compliance.
By working with the right Language Service Provider, businesses can navigate this with ease.
Get in touch with us for a free consultation on translations for DPDPA compliance.