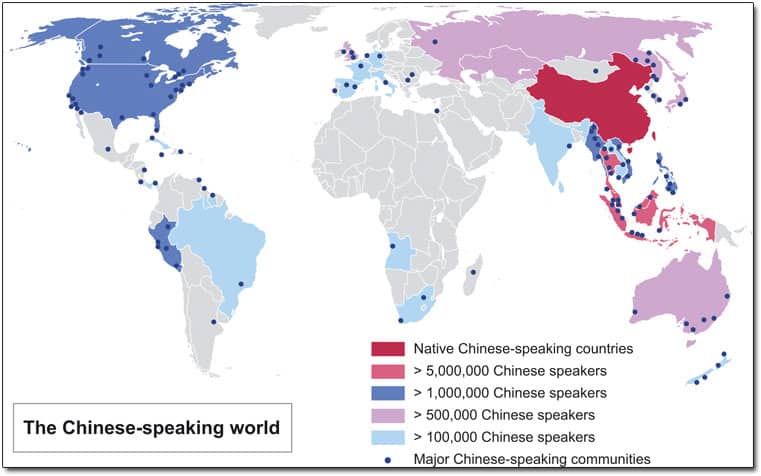
Chinese is the language with the most native speakers in the world. Over 1.3 billion people speak the language globally. What’s more, there are more than 800 million active internet users that speak Chinese, making Chinese the second most widely used language after English on the internet.
Indeed, the market of Chinese-speaking people is massive, however, due to the language and cultural barriers, it is not easy to reach these 1 billion potential customers.
Is There Such A Thing As the Chinese Language?
Chinese refers to several different dialects that have a common origin. Despite their common roots, these dialects are not necessarily mutually intelligible.
Undoubtedly, this hinders communication between speakers of different Chinese dialects and poses a dilemma for companies looking to localize for that region.
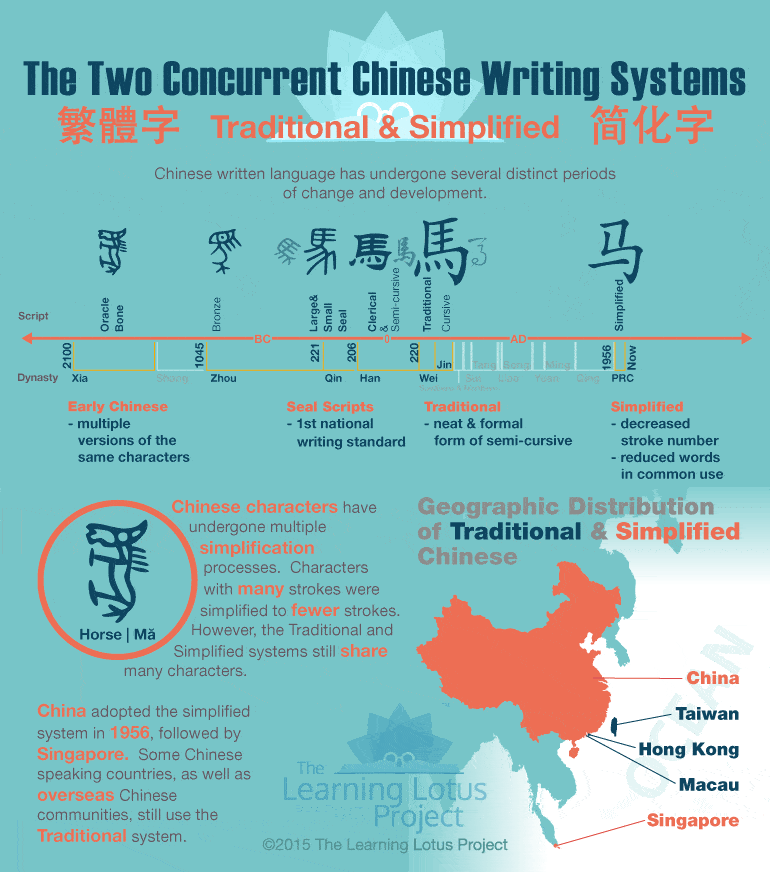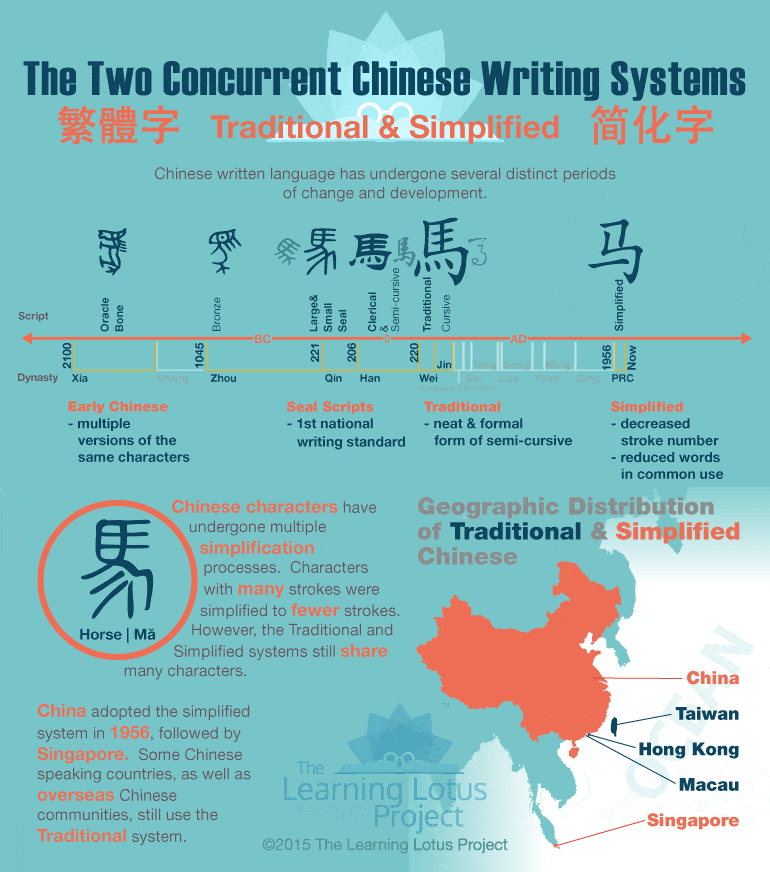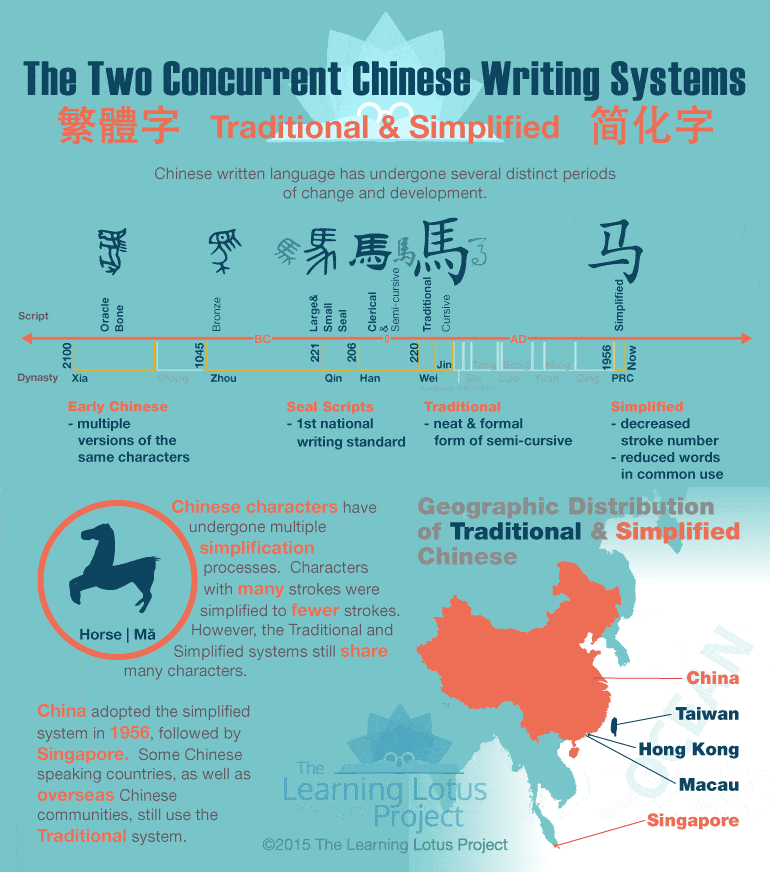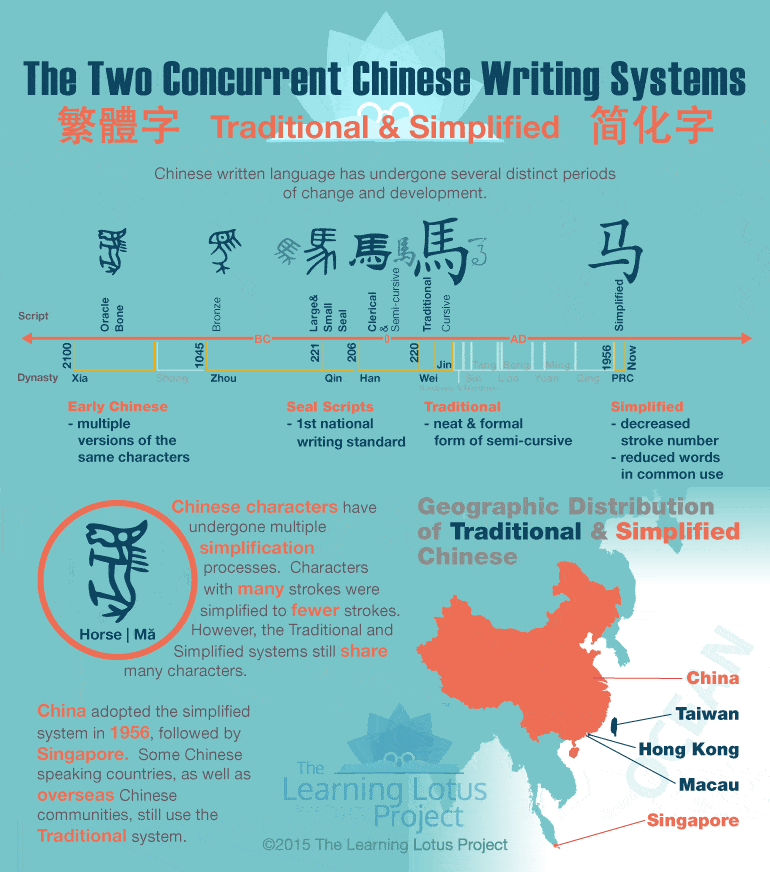
The way Chinese is written differs across the country. There are many different dialects, but there are only two primary written forms: Traditional and Simplified Chinese, which can be used when writing in any Chinese dialect.
Want to learn more about Simplified and Traditional Chinese?
In the following blog, we have compiled everything you need to know about the two written forms of Chinese so that you can pick the right one for your content!
Also Read: Doing Business In China, The Cultural Difference You Need To Know
The History Of The Chinese Language & Its Dialects
Chinese language is a group of different dialects with common roots and various degrees of mutual intelligibility.
Chinese is a logo graphic language, meaning that it has no alphabet as English, for instance, but uses characters to represent particular concepts.
The language is among the oldest languages with over six thousand years of history. Over 3,000 years ago, the Chinese started using pictographs or pictures, carved into animal bones, representing different objects.
Since then, these pictographs have evolved into the Chinese characters we know today. There are approximately 10,000 characters in the Chinese writing system.
There are 7 main dialect groups that were created as a result of the development of the Chinese language. In other words, each group contains Chinese dialects that are, more or less, mutually intelligible and have a lot of common features.

Also read: How Do ELearning Videos Benefit From Multilingual Subtitles
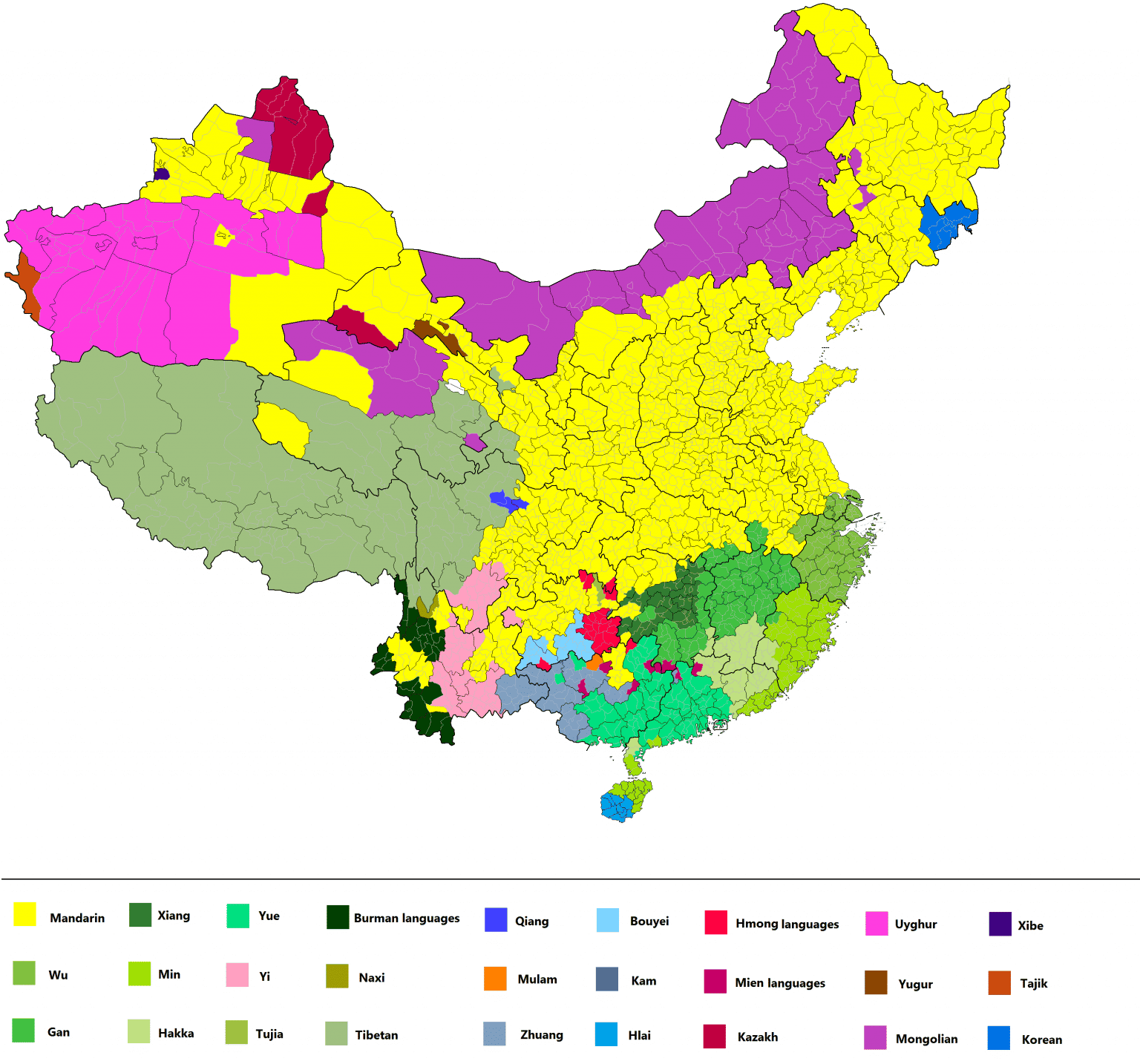
There are quite a few Chinese dialects out there. But you have to keep in mind that all of them are only spoken. When you’re translating your written content, you don’t need to worry about all the dialects.
Also Read: Language Vs Dialect Vs Accent – What Is The Difference?
There are two primary written forms: Simplified and Traditional Chinese. But which one is the right choice when you are translating from English to Chinese.?
Keep reading to find out!
Simplified Vs Traditional Chinese – History
As you already know, Chinese has over 10,000 characters or logographs to write single and multi-character words.
Traditional Chinese consists of orthodox characters that have been used for thousands of years. Simplified Chinese, as its name suggests, uses simplified versions of the Traditional Chinese characters.
How did that happen? Why are there two written forms of the same language?
When the People’s Republic of China was established in 1949, the overall literacy rate in the country was very low – around 20%.
The government believed that the reason behind these statistics was the fact that Traditional Chinese characters were too complex. As a result, the Chinese government launched a massive campaign, promoting literacy and education through a new, simplified writing system.
This new version contained approximately 2,000 modified characters. This modification was primarily done by reducing the number of strokes in a character. The new modified characters were called Simplified Chinese.
Also read: Subtitles vs Closed Captions: Everything You Need To Know
Subtitles vs Closed Captions : Everything You Need To Know
During the ’50s and ’60s, Simplified Chinese was adopted in mainland China, Singapore, and Malaysia.
Traditional Chinese remained the main written form in Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Macau.
Differences Between Simplified & Traditional Chinese
Traditional and Simplified Chinese showcase significant differences in various aspects. In this section, you will find a summary of the most divergent features of both varieties.
- Character structure.
Simplified Chinese uses fewer strokes than the Traditional writing form. For instance, the verb ‘send’ can be translated as the character 发 in Simplified Chinese, which, in turn, equates to 髮 or 發 in Traditional Chinese.
- The number of characters.
Overall, Simplified Chinese has fewer characters. When this new form was created, some traditional characters were merged. Traditional Chinese uses a single character to refer to a specific word or part of the word.
Simplified Chinese, on the other hand, may represent a few different words with a single character.
For example, in the phrase 头发发白, meaning “hair turns gray,” in Simplified Chinese, the two characters in the middle are identical, but still have different meanings.
Since Traditional Chinese represents each word with a unique character, the same phrase would look like this: 頭髮發白.
- Vocabulary and character sequence.
There are certain differences between Traditional and Simplified Chinese in terms of words and character sequence.
For instance, each variety uses different characters for the same word: “video” can be represented as 视频 in Simplified Chinese, while its equivalent in Traditional Chinese looks like 影片.
In other cases, the same characters are used to express the same word, but with a reversed sequence: compare the word “authentic” in Simplified 地道 and Traditional Chinese 道地.
Another possible scenario is that the same character sequence might have a different meaning in each variety. For example, 土豆 means potatoes in Simplified Chinese, while in Traditional Chinese, it means peanuts.
- Text flow.
Yet again, Simplified and Traditional Chinese showcase considerable differences in regard to text flow.
Simplified Chinese has a horizontal text flow, while Traditional Chinese can be written either vertically or horizontally. It can even flow in both directions on the same page.
- Punctuation.
Both Simplified and Traditional Chinese have different punctuation rules.
For instance, in Simplified Chinese, the Western-style quotation marks “…” and ‘…’ are commonly used.
In Traditional Chinese, quotation marks look pretty different: single quotation marks are represented as「…」 and double as『…』.

- Ease of learning.
It is hard to estimate which variety is easier to learn. Some claim that Simplified Chinese is much easier to learn because its characters have fewer strokes.
Others argue that Traditional Chinese characters might seem daunting, but are easier to learn due to certain similarities between the form of the character and its meaning (but only in some cases!). Many of these links are absent in Simplified Chinese.
For example, in Traditional Chinese, the character 門 refers to “a door,” while the character 開 means “to open,” while the character 關 means “to close”. As you can see, the same component is used in each of these related logographs.
In Simplified Chinese, there are different characters for each of these words: 门 (door), 开 (open), 关 (close).4
Overall, Simplified Chinese is taught in most language programs for international students. Even at Chinese schools, the more common variety that is taught is Simplified Chinese.
Which One To Pick For Your Translation
Generally, it can be said that Simplified Chinese is officially used in mainland China and Singapore. It is also often used by the Chinese community in Malaysia.
What’s more, Simplified Chinese is used when communicating with international organizations such as the World Bank and the United Nations.
Simplified Chinese is the norm in Mainland China, there are approximately 1.3 billion people who use this variation. The number of people using Traditional Chinese is much lower, although there are no official statistics.
Traditional Chinese is only rarely used in Mainland China. Most of the Traditional Chinese characters are still readable by most people in this region since classical Chinese texts are in this script. Still, Traditional Chinese is avoided in favor of Simplified Chinese.
Traditional Chinese, on the other hand, is used in Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Macau. In this regard, you should keep in mind that Taiwan and Hong Kong have developed their own variations of the Traditional Chinese writing form. As a result, there are some terms that are unique for each region.
Both varieties are mutually intelligible to a high degree. However, Taiwanese people would recognize the Hong Kong variety right away, and vice versa.
Thus, when translating, it is always best to choose a variety that is native to your target audience.
Especially when it comes to Taiwan and Hong Kong, make sure that you can provide translations in the Traditional Chinese variety of each region.
When Translating For a US Audience
The third-largest immigrant community in the US is Chinese, following Mexicans and Indians. The largest Chinese communities are located in California (32%) and New York (19%).
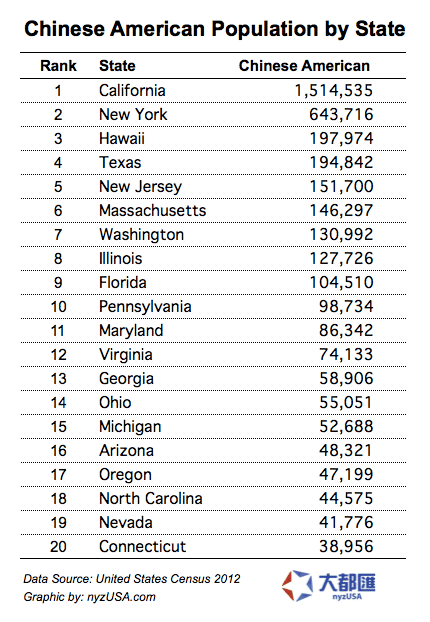
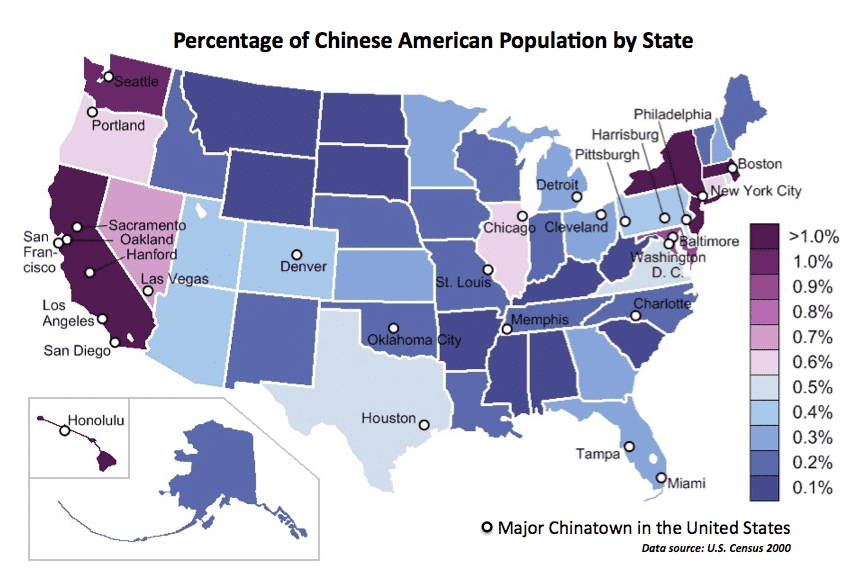
Since these communities have been established before the advent of the Simplified Chinese writing system, many Chinese immigrants use Traditional Chinese.
Still, you have to keep in mind that the more recent immigrant influxes have led to the diversification of the Chinese populations across the US.
Therefore, the best way to successfully reach Chinese communities in the US is to translate your content into both Simplified and Traditional Chinese. However, the more commonly used variety is Traditional Chinese, since most of the immigrants came to the US before the establishment of Simplified Chinese.
Also Read: The Top Languages Spoken In California
So which variety should you choose?
To answer this question, you have to think about your target audience: where it is situated and their age group.
Generally, elderly people know both Traditional and Simplified Chinese, while younger generations understand Simplified Chinese.
You must also know that people knowing Traditional Chinese can understand the Simplified version as well. However, it is not the other way round.
Simplified Chinese is by far the most widely used variety. Plus, it’s the most commonly used type for international students and it’s fully understandable to those who read Traditional Chinese.
In conclusion
The Chinese language consists of a large variety of mutually unintelligible dialects. However, all the Chinese dialects share two primary common forms of writing: Traditional and Simplified Chinese.
Knowing where each of these writing forms is used is the key to successfully connecting with your target audience. Indeed, each variety is popular in, more or less, clearly divided regions, which in turn makes your choice easier.
However, if you want to reach most of the Chinese population, there is only one way to do it – you have to translate your content into both Traditional and Simplified Chinese.
Setting up or expanding a business in China is not an easy task! However, with the right partners by your side, this whole process can be as easy as a child’s play. This is why you should always look for professionals who can help you with the translation, localization, design, etc., for your business expansion plans.
We’re here to help. Milestone Localization is the leading Translation and Localization Agency In India & UK. Get in touch.