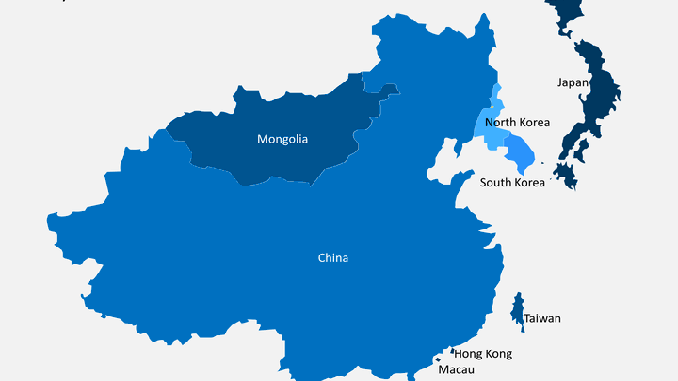
East Asia covers the territory of China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Macau.
The region is not only defined by the geographical location of these countries but also by their cultural and linguistic heritage.
East Asia is the cradle of one of the oldest civilizations in the world. The Chinese civilization was established by the Shang dynasty as early as 1250 BC.
The Korean, Mongolian and Japanese civilizations also date back thousands of years.
East Asia is home to one-fifth of the world’s population. Its strategic location on the Pacific Rim grants the countries of this region the opportunity to connect with the global economy.
Taiwan, China, Japan, and South Korea have established themselves as entrepreneurial and industrial pacesetters beyond just East Asia.
China and Japan are the second and third-largest economies in the world. East Asia is on its way to becoming one of the biggest economic centres in the world.
Are you planning on expanding your business there? Here’s an introduction to the geography and the languages of East Asia.
The countries of East Asia
The region of East Asia consists of 6 countries and is characterized by rapid economic growth.
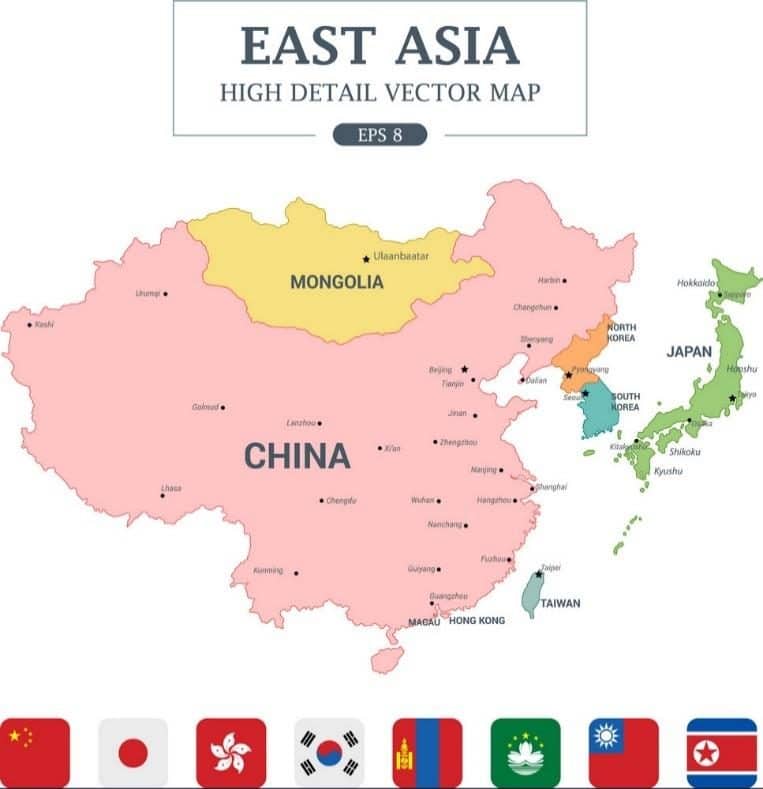
- China: China is the biggest country in the region both in terms of population and territory. Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan are all closely associated with mainland China. China is the most influential country in the region and is expected to become the most powerful economy in the world by 2050.
- Japan: Japan oftentimes refers to as the economic dragon of East Asia. Japanese people have a high living standard which is a result of the country’s economic growth which began in the 1960s. Japan has the third-largest economy in the world.
- Mongolia: As the only landlocked country in the region, Mongolia is highly dependent on its neighbors – Russia and China. What’s more, up to 60% of Mongolia’s external trade depends on China while China receives roughly 90% of Mongolia’s exports. When it comes to Russia, Mongolia relies on its Slavic neighbor for 90% of its energy supplies.
- North Korea: Compared to its neighboring countries, North Korea is rather left behind in regard to its economic development. The country has been under an authoritarian dictatorship since World War II and its isolation has taken a toll on its economical power.
- South Korea: South Korea has seen massive growth since the 1960s. It is now one of the most highly industrialized countries in the world. This growth has been triggered by the abundance of a high-skill and well-educated workforce as well as the rapid development of export-oriented industries. Lately, the focus has shifted to high-technologies industries such as electronics and automobiles.
- Taiwan: In the 1960s the country’s economy underwent spectacular growth and was consequently referred to as ‘the economic miracle’. Since the 1980s Taiwan has taken up the initiative to move on to more knowledge-oriented industries. It has consequently become one of the leading manufacturers of computers and electronics in the world.
Also Read: What Are The Main Languages Spoken In The Middle East
The Biggest Language in East Asia
It probably won’t surprise you to learn that the Chinese language that is the most popular one in East Asia.

Spoken by 1 billion people in Asia and 200 million people worldwide. It is indeed the fastest-growing language in the world!
However, not many people know that there’s no such thing as the Chinese language, but rather this expression used to refer to a number of Chinese dialects, the most popular of which is Mandarin Chinese.
[bctt tweet=” However, not many people know that there’s no such thing as the Chinese language, but rather this expression used to refer to a number of Chinese dialects, the most popular of which is Mandarin Chinese.”]
This is also the official language in China, Hong Kong and Taiwan.
The popularity of the Chinese language is a result of a number of factors. On one hand, the massive population of the country accounts for the great number of Chinese speakers.
On the other hand, the one-of-a-kind economic growth of China has turned the language into a valuable tool for trade and economic relations.
The recent interest in the Chinese language and culture has also greatly contributed to the rising popularity of the language.
Also read: Doing Business In China: Cultural Differences You Need To Know
Dialects of Chinese spoken in different East Asian countries

Chinese is an umbrella term denoting the number of dialects. In East Asia, there are three main Chinese dialects spoken. Have a look:
- Mandarin Chinese. This is the standard dialect of China and spoken by over 1 billion people in the world. Mandarin has four tones and is monosyllabic.
- Cantonese Chinese. This Chinese dialect spoken by 70 million people in Hong Kong, the Guangdong Province of China as well as throughout East Asia.
- Minnan Chinese. Around 50 million people speak this dialect and its speakers mainly situated in the Fujian Province of China, Taiwan, and throughout East Asia. There is also a sub-dialect of Minnan Chinese spoken in Taiwan.
Also Read: How To Localize Your Website For China
Other languages of East Asia

Despite the widespread distribution of Chinese in East Asia , we should not overlook the rest of the languages spoken in East Asia. The region’s linguistic diversity is incredible
- Japanese: This is the national language of Japan and spoken by more than 120 million people. Similarly to Chinese, the term Japanese denotes the number of different dialects. There is the Standard Japanese (hyōjungo) as well as a number of dialects such as Kansai, Osaka, Kyoto, and Tohoku. All these dialects are mutually intelligible with Standard Japanese.
- Okinawan: This language is spoken by less than 1 million people in a few peripheral islands in Japan such as the islands of Okinawa, Kerama, Kumejima, Tonaki, and Aguni. What’s more, there are two distinct varieties of the language – Northern and Central Okinawan. Both of them are listed as endangered languages by UNESCO.
- Korean: Korean, is spoken by around 80 million people worldwide, and most speakers are situated in North and South Korea. In South Korea, it is Seoul’s dialect that primarily uses formal settings while in North Korea – a mixture of Seoul’s dialect and the Pyeongyang region’s dialect.
- Taiwanese: Also known as Hokkien, Taiwanese is the common language in Taiwan and is similar to Traditional Chinese. It is mutually intelligible with Mandarin.
- Hakka: This Chinese variety, spoken by people in Taiwan with ancestry and is one of the national languages of Taiwan
- Mongolian: This language, is spoken by around 6 million people and uses a modified version of the Cyrillic script.
- Portuguese: Incredible, I know! In fact, Portuguese is an official language together with Chinese in Macau – a special administrative region of China. Macau was a former colony of the Portuguese empire until the late 1980s. Still, Portuguese is spoken by only 1% of Macau’s population which is about 680 thousand people.
Also read: Portuguese vs Spanish : Is Spanish Similar To Portuguese
Differences and similarities between Asian languages
The languages of East Asia belong to different language families, however, due to their territorial closeness, there are many common features between them.
The languages of this area tend to be analytic with many similarities in their tone and syllable structure.
The influence of the Chinese language

During the 1st millennium AD, Chinese culture became the dominant power in the region, and thus, Classical Chinese got adopted by Korean and Japanese scholars.
Many Chinese vocabularies were integrated into the languages of these countries.
The Chinese script was also adopted by the Japanese and Korean languages, although nowadays the use of this writing system is restricted to only a few spheres such as university learning, historical study, and newspapers (only in Korea).
The East Asian & Southeast Asian language families
East Asia is an incredibly diverse region and thus, it will be hard to consider all language families in this area. Still, here is a concise summary of the biggest ones:
- Sino-Tibetan: All varieties of the Chinese language belong to this group.
- Austronesian: It’s believed that this language family has spread from the territory of Taiwan to the rest of Asia and the island in the Pacific and the Indian Oceans.
- Altaic: This language family consists of the Turkic, Mongolic, and Tungusic languages. Some linguists claim that Koreanic and Japonic languages also belong to this language family, but this theory has refuted a long time ago. The language of this group tends to be atonal, polysyllabic, and usually follows subject-object-verb word order.
- Japonic: Oftentimes referred to as the Japanese–Ryukyuan language family, it is comprised of Japanese as well as the Ryukyuan languages, only spoken in the Ryukyu Islands.
- Koranic: This is a rather small family consisting of Korean and the language of Jeju Island, which is a Korean dialect spoken in South Korea.
Also read: Language vs Dialect vs Accent: What Is The Difference?
Connect With East Asian Customers In Their Native Languages.
Milestone helps you seamlessly translate content & localize your website, products, and services for more reach, better conversions, and greater sales.
Are East Asian languages mutually intelligible?
Chinese certainly has left its mark on some East Asian languages in terms of script and vocabulary.
Also read: Must Know Things About Korean Business Etiquette & Culture
However, the great influence of Chinese over Korean and Japanese does not mean that these languages are mutually intelligible.
What’s more, each of these languages belongs to a language family of its own and thus, has developed its vocabulary and grammatical structure differently and, to some extent, independently from each other.
Moreover, the Chinese writing system was adopted and modified to meet the “needs” of the Korean and Japanese languages, so technically, they don’t use the Chinese script, but rather a variation of it.
Overall, it is a common misconception that Chinese, Japanese and Korean are mutually intelligible. In reality, these are three completely different and rather unrelated to each other.
[bctt tweet=”Overall, it is a common misconception that Chinese, Japanese and Korean are mutually intelligible. In reality, these are three completely different and rather unrelated to each other.”]
Is English spoken in East Asia?
Surprisingly or not, English is so popular in this region that East Asian English is considered an English variety of its own!
However, the overall proficiency is not as high. Below you can see a comparison of all countries in Asia and their English proficiency index:
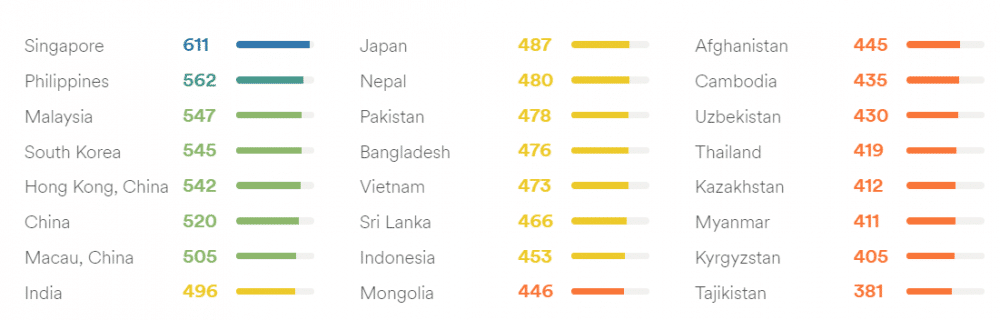
A very prominent increase in the number of English students can be observed recently. Around 350 million people study English in China. English is also one of the official languages of Hong Kong.
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) in Japan has officially started an English-speaking project.
The aim of this initiative is to increase the number of courses taught in English at Japanese universities and to generally internationalize higher education in Japan.
What’s more, Korea and Taiwan are constantly trying to improve their primary school English language teaching to enhance their national competitive abilities in the global world.
Due to the ongoing globalization as well as the fact that East Asia is willing to accept foreign investors and buyers, English has become a valuable skill.
Thus, expanding the region’s economic growth is closely related to promoting learning English.
East Asia is a region that unites culturally and linguistically diverse countries. The English learning policies in China, Japan, Korea, and Taiwan are just a single example of the region’s enthusiasm to join the global world.
However, the internationalization of these countries is just beginning and it will take years until English has established itself as a major language.
East Asian countries are seeing rapid economic growth and present big opportunities for business expansion.
To be successful in this region, companies must translate and localize their products and communications. If you’re looking to tap into this market of 1.7 billion people, get in touch.
Also read: 11 Elements To Consider For A Successful Localization Strategy
Connect With East Asian Customers In Their Native Languages.
Milestone helps you seamlessly translate content & localize your website, products, and services for more reach, better conversions, and greater sales.




