Language vs Dialect vs Accent- have you ever wondered about the difference and relationship between these terms? Keep reading to get the answer to your question.
Languages are living creatures – they never stop evolving. The more widely a language is spoken, the more changes it undergoes. Out of languages, develop dialects and accents. These, in turn, could form new languages as well, and the cycle continues.
Centuries ago, Latin was the most widely spoken language on the European continent. As the Romans conquered new territories, they imposed their language on these newly acquired lands and their people. The Latin language mixed with the local languages resulted in several Latin dialects.
Also Read: Beginners Guide to Website Translation for Latin America
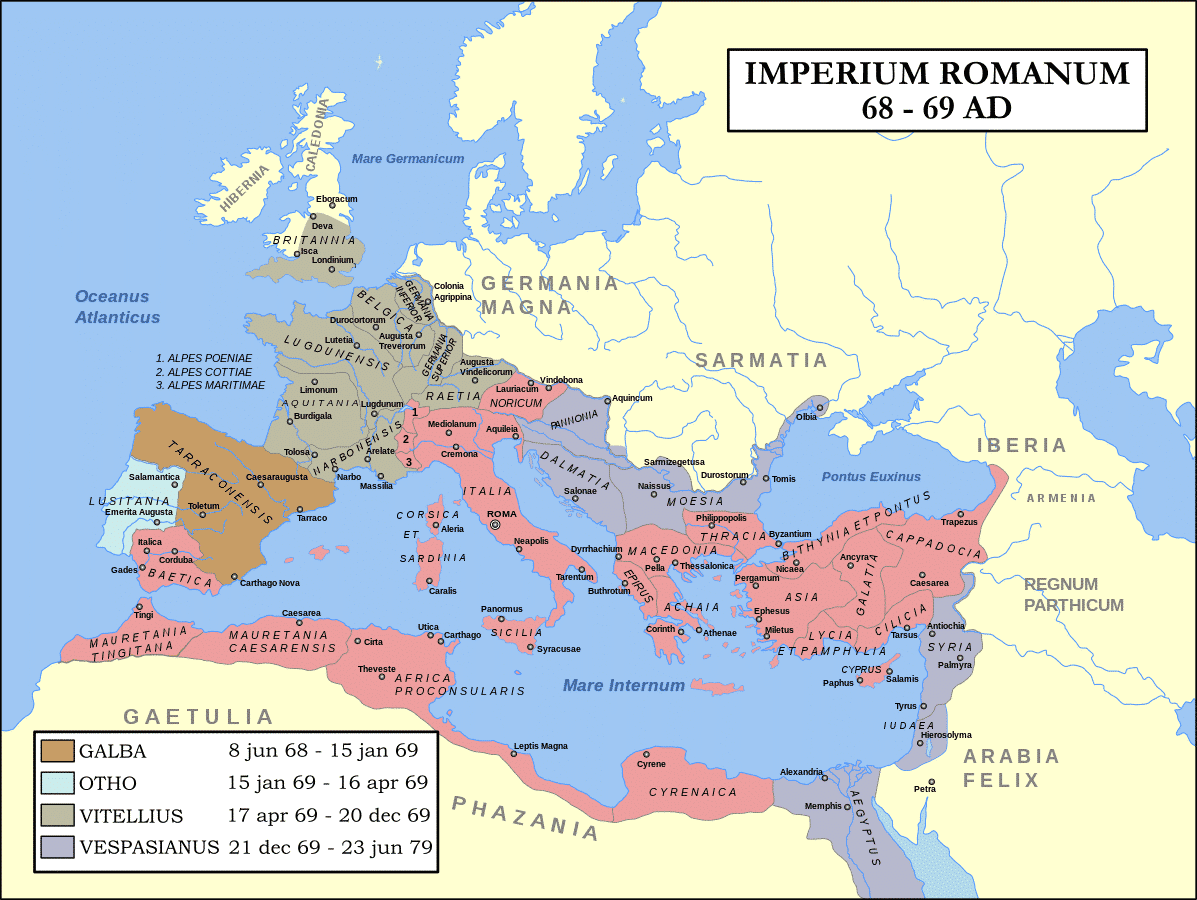
At one point, Millions of people spoke Latin. But the final days of the Roman Empire came, and Latin lost its prestige. Eventually, Latin died out. However, its dialects formed languages that we today know as French, Italian, and Spanish.
French, Italian, and all Romance languages have their own dialects that have developed over time and keep changing.
Also Read: Italian vs French: How Different and Similar are these Languages?
As you can see, it’s a rather complicated process that makes it rather difficult for one to differentiate between Language vs Dialect vs Accent
Do you want to know more on the subject? Then, keep reading!
1. What is a language?
Simply put, languages are our most valuable communication tool.
But what exactly is a language?
A language is a system that consists of different elements such as signs (letters or characters), sounds, grammar elements, vocabulary, etc. Since it’s a system, it has a structure.
For instance, we build sentences based on grammatical rules. In English, they are specific – the verb always follows the subject. However, in Bulgarian, one can move the sentence’s part more freely.
Also Read: 10 Untranslatable Bulgarian Expressions
So, the structure of a language depends on its grammatical rules. These rules, as almost all elements of a language (e.g., sounds, alphabet, vocabulary, etc.), result from linguistic changes, but you will learn about this later.
Languages have different modes of transmission. Most languages utilize particular writing systems that allow people to read or write in a specific language. We can also produce words through different sounds and thus, speak or listen to a language.
It is essential to note that an alphabet is not necessarily a common feature of all languages. Some Modern South Arabian languages spoken in Yemen and Oman are primarily unwritten, meaning they have no script. Examples include Mehri, Hobyot, Harsusi, Soqotri, Shehri, and Bahari.
Sign languages are examples of languages that use signs made with hands instead of sounds for people to communicate. Sign languages are natural and develop independently. This means that the American sign language is an independent entity and does not depend on English. In other words, they have different grammar, vocabulary, etc.
There are different writing systems for languages. Some use scripts such as Latin or Cyrillic, while others like Chinese use special characters that stand for a particular word. The Braille alphabet, on the other hand, utilizes three-dimensional characters.
Also Read: Languages Spoken In Texas & Its Bilingual Education System
Common features of languages
As you can see, human languages are a unique communication tool. Despite their incredible diversity, all languages possess the following features:
- Productivity. A language is an infinite system and is constantly evolving. One can create new words, grammar rules, etc., endlessly. On the contrary, bees and other animals’ communication systems can express only a limited set of ideas. We have a finite set of elements (signs, such as letters and sounds) that we can combine to create new features to help us communicate our ideas better. For instance, COVID-19 wouldn’t ring a bell in a 19th-century writer’s mind, but we have created this name to refer to a recently discovered virus.
- Displacement. Human languages allow us to talk about unreal ideas and concepts. This means we can talk about the future, the past, or even about impossible things like living on another planet or visiting imaginary worlds. Animals, on the contrary, can communicate only about the present moment.
- Social conventions. Languages rely on social conventions to ensure successful communication. This means that all speakers of English, for instance, know that an ergonomic chair means a four-legged object on which you can sit. Such social conventions ensure smooth and straightforward communication.
- Learned. Human languages can be learned, which is a great asset, especially in globalization!
Overall, languages are complex communication systems, which despite their immense diversity, share a few common, intrinsic values.
2. What is a dialect?
A single language can often have numerous dialects. Based on regions, dialects are differentiated (British vs. American English) or social (Viennese dialect vs. High or Standard German) differences between the speakers.
But let’s start with a short definition: A dialect is a variety of language that differentiates in terms of phonology, phonetics, vocabulary, and grammar.
An easy example of dialects of the same language would be British and American English. These two varieties exhibit differences in terms of phonology (British vs. American /r/ sound), phonetics (realize vs. realize), and vocabulary (biscuit vs. cookie). There are even slight differences in grammar: British people are more likely to use “shall,” while American people often opt for “will” or “should,” for instance.
Nevertheless, British and American English share many similarities, such as alphabet, general vocabulary, and grammatical rules, which is why they are dialects (also referred to as varieties) of the same language – English. English, as the most widely spoken language, probably has the maximum dialects.
Other common languages with dialects would be Arabic, Hindi, and Chinese. They are spoken by millions, if not billions of people, in many regions. For instance, Chinese has hundreds of dialects such as Mandarin, Wu, Gang, Hakka, Min, Xiang, Yue, Jin, etc.
Before its standardization, in India, several spoke dialects of Hindi. The most prominent ones were Avadhi, Braj Bhasha, Awadhi, Maithili, and Braj. However, it can be barely heard nowadays due to the rise of standardized Hindi.
Also Read: Do These 10 English Words Have a Hindi Translation?
As for Arabic, its dialects often get compared to the Romance languages. Generally, French is somewhat incomprehensible to Italian or Spanish speakers but relatively easy to learn. Similarly, Moroccan Arabic is comprehensible for people from Maghreb, Africa, but this is not the case for the Arabs in Mashrek or the eastern part of the Arab world.
3. What is an accent?
The last one to cover is the accent. People frequently confuse accent and dialect, but remember – these are two different things!
An accent refers to the pronunciation of language or how a person produces a particular language’s sounds.

In other words, how we pronounce a particular term is an accent. For instance, pronouncing vase as /vahz/ in British English or /veis/ in American English is an example of an accent.
For instance, we can refer to an accent as foreign. I, as a Bulgarian, speak German with a foreign accent since it is not my mother tongue, and I haven’t yet fully learned the German pronunciation.
While accents are often associated with foreigners, it is not always the case—for instance, many people like the sound of the British accent.
But how can one differentiate between an accent and a dialect? We will explain it in detail later in the article.
Connect With your Customers In Their Native Languages.
Milestone helps you seamlessly translate content & localize your website, products, and services for more reach, better conversions, and greater sales.
4. Language vs. Accent vs. Dialect – A Matter of Linguistic Change and Borrowing
As you can see, a dialect can be regarded as a variety or a subtype of a language, while accent has mainly to do with pronunciation and how sounds get pronounced.
That being said, linguistic change lies at the center of the emergence of accents, languages, and dialects. Due to the complexity of the language system, change happens to different elements, sometimes simultaneously, sometimes not.
What’s more? when a language, spoken in many locations (e.g., Spanish in Spain, Mexico, Argentina, Chile, etc.), change happens independently.
Also Read: An Introduction to Universal Spanish
For example, even though the Spanish spoken in Spain and Mexico have common roots, they developed independently of one another for centuries. Eventually, one of the most significant differences between the two varieties occurred – the pronunciation of in /z/ and /c/ before an “i” or “e.” Indeed, when there is such a great distance between two locales, the differences are bound to be more significant since there is little point of contact.

Generally, linguistic changes happen slowly and gradually as they accumulate to form new dialects (e.g., Mexican Spanish). Dialects, however, are impure since they contain a lot of words from the local jargon, slang, argots, pidgins, etc.
For instance, Mexico has a rich pre-Hispanic culture. Thus, there are words in the Mexican Spanish language directly derived from the Yucatec Maya, Nahuatl, and other indigenous cultures. Such words are cenote (from the Yucatec Maya word ts’onot meaning underground water), aguacate (avocado), and cacahuate (peanut).
Also Read: Spanish Localization: Should You Localize into LA or European Spanish?
Another way of extending the vocabulary of a particular language is by borrowing words. For instance, the word caste got borrowed by the British colonizers from Hindi to describe the caste system in India.
Immigration has a considerable impact on languages in this regard. For instance, since the 1990s, millions of people from the Balkan peninsula have found a new home in Germany. This has, in turn, greatly influenced the German language and its vocabulary, in particular.
Nowadays, most German slang words such as para or Mashallah have foreign roots. For instance, para is a slang word for money in Bulgarian, Serbian, and other South Slavic languages. On the other hand, Mashallah is a Turkish saying that means Bravo! or Well done!.
Despite their foreign origin, one can hear many German youngsters using these expressions in their everyday speech today.
Overall, languages got influenced by the people they are being spoken by. So, substantial immigrant communities will inevitably directly impact the local languages of their host countries.
5. Language vs. Dialect – a matter of standardization
When institutions use a dialect in official documents, legal contracts, or, generally, in literature – it becomes a standard language. So, when a particular lingo is used predominantly by the rich, powerful & educated members of society.
The variety got associated with these qualities & becomes a model or standard for the rest of the community.

Also read: ICF Translation: Importance, Requirements & Best Practices
To establish a specific dialect as the norm, one should create dictionaries, grammar books, and other reference works. Governmental, scholarly, and literary works in the particular dialect, on the other hand, function to popularize this variety. This variety is then taught at schools and accepted as formal communication events.
In other words, the purpose of this process of standardization is to create one primary, dominating linguistic form (in other words, a dialect) while eliminating the deviating ones.
But if a language is a standardized dialect, how can we distinguish between the two?
One way is to consider their mutual intelligibility. Usually, speakers of different dialects of the same language can understand each other.
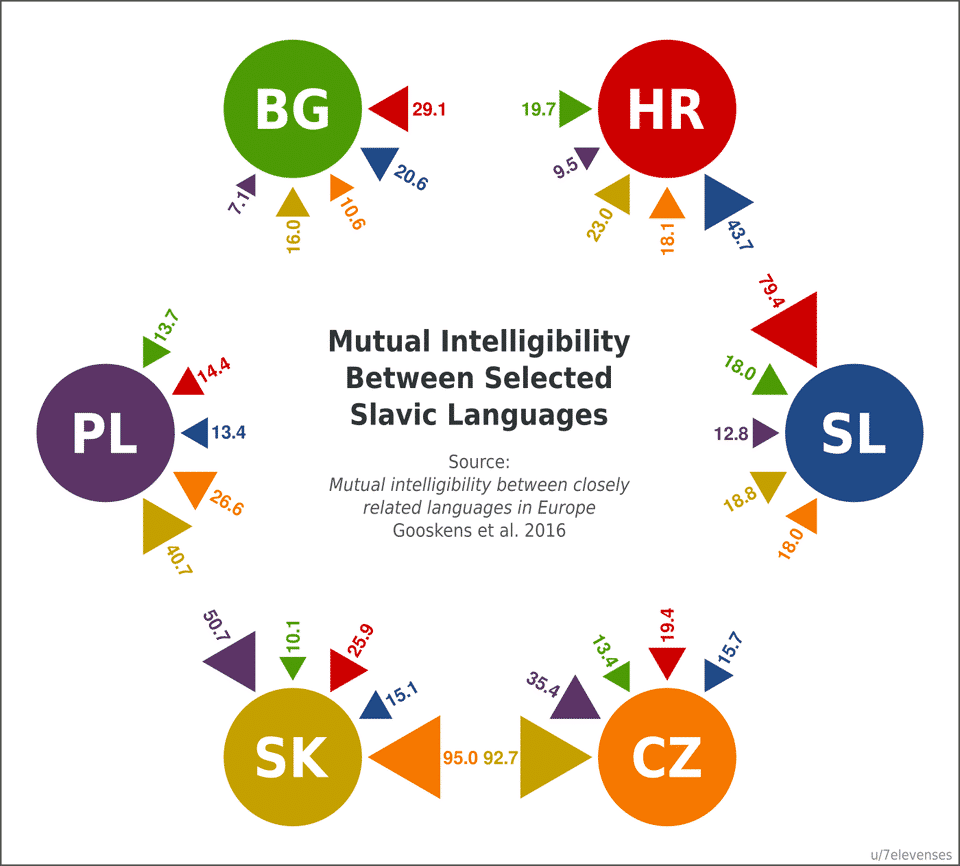
However, this is a somewhat relative criterion to base your judgments on. Take, for example, some closely related languages such as Bulgarian and Serbian. Although these are separate languages and not dialects, their speakers can communicate with each other, more or less, freely. The same goes for Italian and Spanish speakers.
Overall, simply relying on mutual intelligibility is not enough. A more solid and practical approach would be through institutions.
As you have already read, some dialects are standardized and thus, recognized as official languages. This standardization happens through institutions, as well as through the publication of scholarly and literary works. So, if you want to distinguish a speech from a dialect, you have to ask yourself whether that language is officially recognized in any country around the world.
For instance, is Hawaiian Pidgin a language like English?

No, since any institution in the world does not use it. On the other hand, English, recognized as an official language in several countries.
But what about Latin – a dead language? Or Tulu – a Dravidian language spoken in India, with no official status?
As you can see, this approach is also flawed. However, it leads us back to our initial supposition that a language is simply a dialect with prestige due to the official recognition of some institutions.
6. Accent vs. Dialect – A Matter of Perception
In linguistics, accents are often perceived as part of a dialect. Another point of view suggests that accents only consider the pronunciation, while dialects are much more complex, referring to grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation.
What’s more, dialects are often associated with the locals. We say Bavarian dialect or Viennese dialect as the local varieties of the German language. However, when we say German accent, we mean something very different.
Since an accent is often considered foreign, a German accent would mean a German person speaking English with a German accent. On the other hand, we would not say that a German person speaks with a Bavarian accent, but that they speak the Bavarian dialect.
Also Read: German vs Russian: Which Language Has a Brighter Future?
As a rule of thumb, an accent is often associated with the foreign, while dialect is local. Still, the lines in between can be a bit blurry, so keep that in mind!
In Conclusion
Languages never cease to evolve into different dialects or accents. These, in turn, could also develop as distinct languages, so on and so forth… What is important to remember is that this so-called linguistic change can take years, if not decades or even centuries, to happen.
The speakers of a language usually propel change. Overall, understanding the dynamics of linguistic change will help you immensely differentiate between language, dialect, and accent.
Connect With your Customers In Their Native Languages.
Milestone helps you seamlessly translate content & localize your website, products, and services for more reach, better conversions, and greater sales.